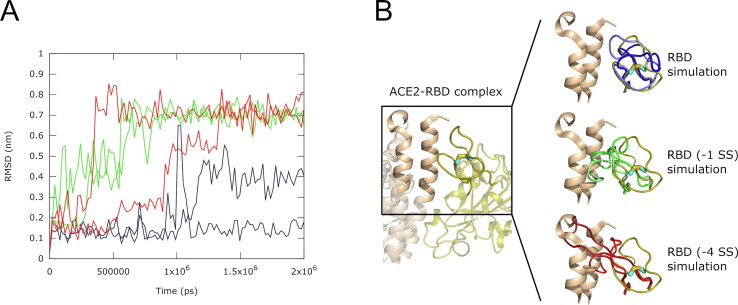
Figure 2.
RMSD and snapshots of the conformation of the RBD ACE2-binding surface loop, residues 454–492, along six molecular dynamics trajectories at 37 °C. (A) Root mean square deviation (RMSD) of the Cα atomic coordinates (nm) vs. time (ps). The data for the RBD with 4 S—S bonds is colored blue; the RBD without C480-C488 bond – RBD (−1 SS) – green; the RBD with all four bonds reduced – RBD (−4 SS) – red. Two curves are shown for each model, corresponding to two independent simulations. The RMSD values show that models with the reduced C480-C488 bond have higher levels of structural deviation in the ACE2-binding surface loop 454–492; (B) (left) The loop-focused view of the crystal structure of the Spike RBD – ACE2 complex in ribbon representation. Only a part of the structure is shown. The Spike RBD domain is colored olive, while ACE2 is colored wheat. The C480-C488 S—S bond is shown as a wire with cyan carbon and yellow sulfur atoms. (right) Snapshots of molecular dynamics simulations, showing the conformations of the ACE2 – binding loop. The conformations from the RBD simulations are shown in shades of blue, RBD (−1 SS) – shades of green and RBD (−4 SS) – shades of red and are superimposed on the experimental structure.