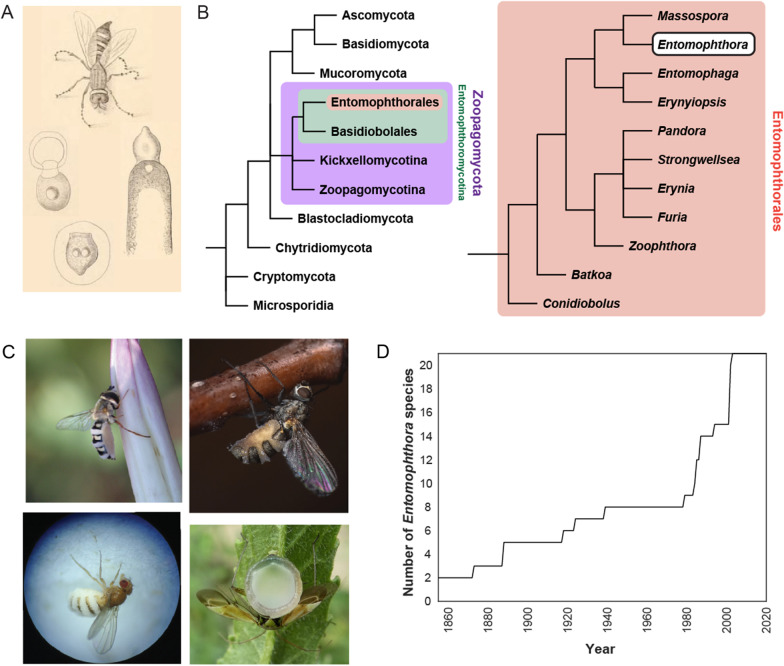
Fig. 1.
What is Entomophthora? A Early camera lucida drawings of E. muscae (Cohn 1855). Clockwise from top: House fly killed by E. muscae, conidiophore forming a primary conidium, ejected primary conidium surrounded by cytoplasmic halo, primary conidium giving rise to secondary conidium. B (Left) Schematic fungal cladogram based on (James et al. 2013; Spatafora et al. 2016); branch lengths are not proportional to genetic distances; the phylum Zoopagomycota encompasses the division Entomophthoromycotina, which in turn contains the order Entomophthorales. (Right) Schematic cladogram of order Entomophthorales based on (Gryganskyi et al. 2012); the position of Entomophthora is highlighted near the top. C Insects killed by fungi in the genus Entomophthora. Clockwise from top left: syrphid killed by E. syrphi, muscoid killed by E. muscae, mirid killed by E. erupta, Drosophila melanogaster killed by E. muscae isolate ‘Berkeley’. Images provided under CC BY-NC license credits by iNaturalist users silverseastarsong (James Bailey), xx7trey (Trey Wardlaw) and dlbowls, respectively. Bottom left image provided by Carolyn Elya. D Number of currently recognized Entomophthora species over time