Figure 3. N-linked glycans modulate neuronal activity.
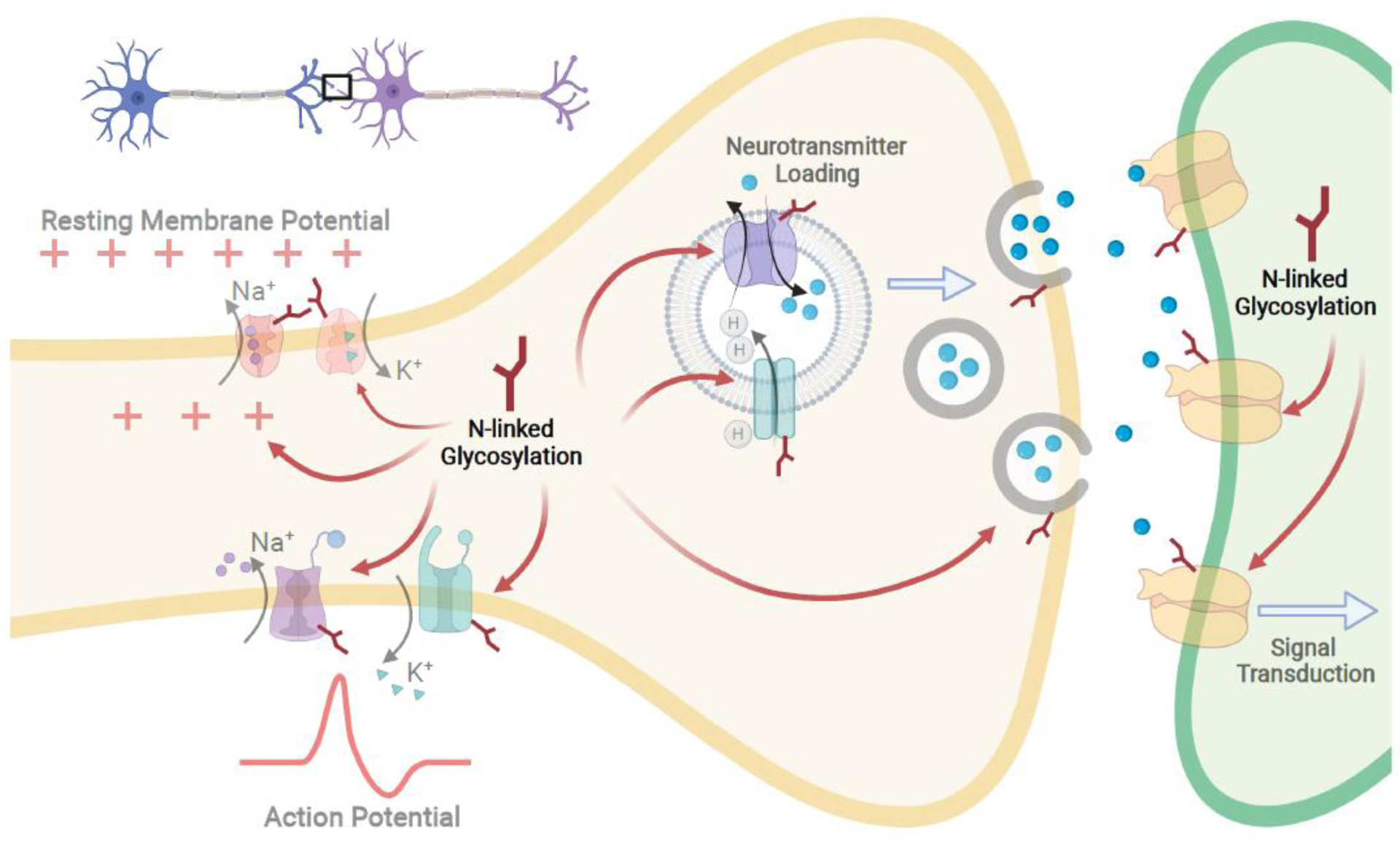
Neuronal processes translate into brain function through synaptic transmission. These processes include maintaining resting membrane potential, axon firing through action potentials, neurotransmitter loading in vesicles and their release, and ultimately neurotransmitter and receptor binding leading to signal transduction. All of these processes are regulated or fine-tuned by N-linked glycosylation. Thus far, Na+/K+ ATPases, voltage gated ion channels (VGICs), and antiporters on synaptic vesicles and neurotransmitter receptors are all reported glycoproteins, and N-linked glycosylation assists in their folding and trafficking, but also modulate their activity. Therefore, proper control of N-linked glycosylation is critical for neuronal function.
