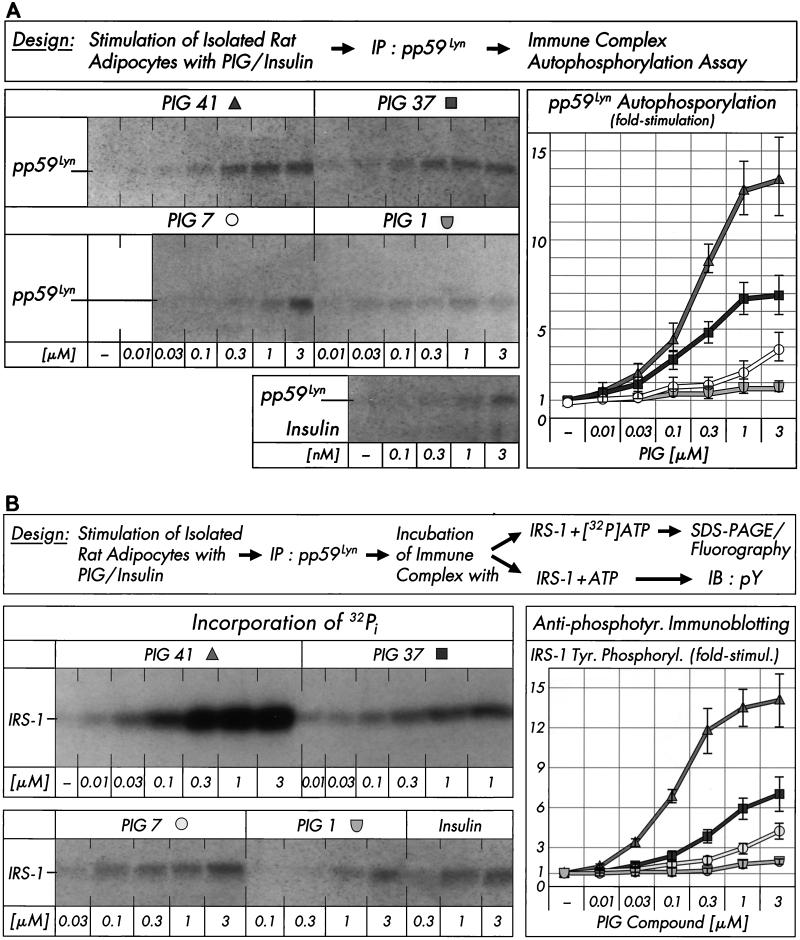
FIG. 3.
Effect of PIG compounds on pp59Lyn activity. Isolated rat adipocytes were incubated in the absence or presence of increasing concentrations of PIG compounds or human insulin. pp59Lyn was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-pp59Lyn antibody from defatted cell lysates and then subjected to immune complex kinase assays for autophosphorylation by incubation with unlabeled ATP (A) or phosphorylation of recombinant human IRS-1 by incubation with either [32P]ATP or unlabeled ATP (B). Phosphorimages of a typical experiment are shown (left sections) repeated three times with similar results. Basal pp59Lyn autophosphorylation and IRS-1 tyrosine phosphorylation were rather low and comparable to those observed in the presence of up to 0.01 μM PIG 37, 7, and 1 (which are shown instead of the basal phosphorylations only). Quantitative evaluation is given as fold stimulation (mean ± standard deviation [right sections]). Basal phosphorylation is set at 1 in each case. Insulin increased autophosphorylation of pp59Lyn and tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS-1 (according to antiphosphotyrosine immunoblotting [IB]), respectively, 1.6- to 1.4-fold at 0.3 nM, 2.2- to 2.7-fold at 1 nM, and 3.1- to 2.9-fold at 3 nM versus the basal level.