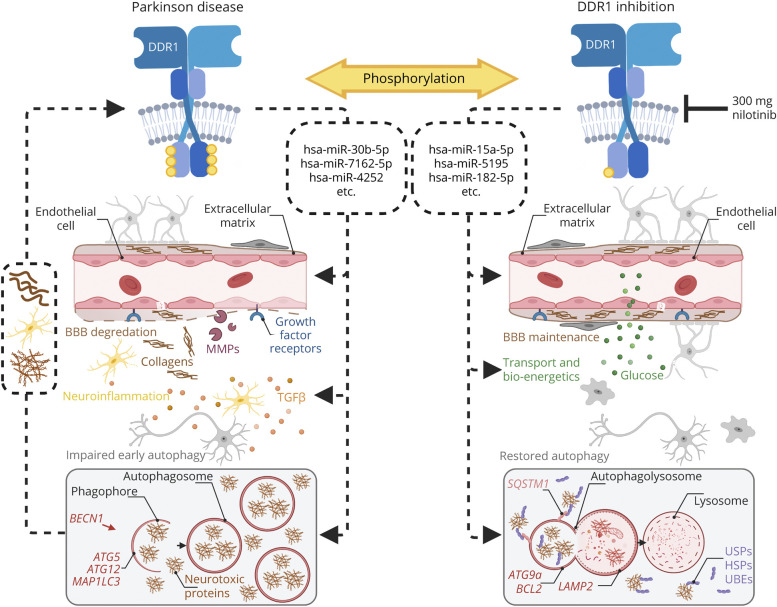
Figure 5. Summary of Mechanism for miRNA in Parkinson Disease and Response to DDR1 Inhibition.
(A) Discoidin domain receptor1 (DDR1) is overactivated, and several miRNAs, including hsa-miR-30b-5p, hsa-miR-7162-5p, and hsa-miR-4252, regulate several key Parkinson disease-associated pathologies, including blood-brain barrier (BBB) degradation, neuroinflammation, and impaired early autophagy. These pathologies may then promote DDR1 activity, creating a negative feedback loop. When DDR1 is inhibited, via nilotinib, 300 mg, we find that the miRNA differentially expressed miRNAs (DEMs) in placebo are reversed. In addition, we find that miRNAs, including hsa-miR-15a-5p, hsa-miR-5195, and hsa-miR182-5p, positively affect BBB maintenance, transport of glucose across the BBB, and bioenergetics, and restore autophagic flux. This schematic was created using BioRender.com.