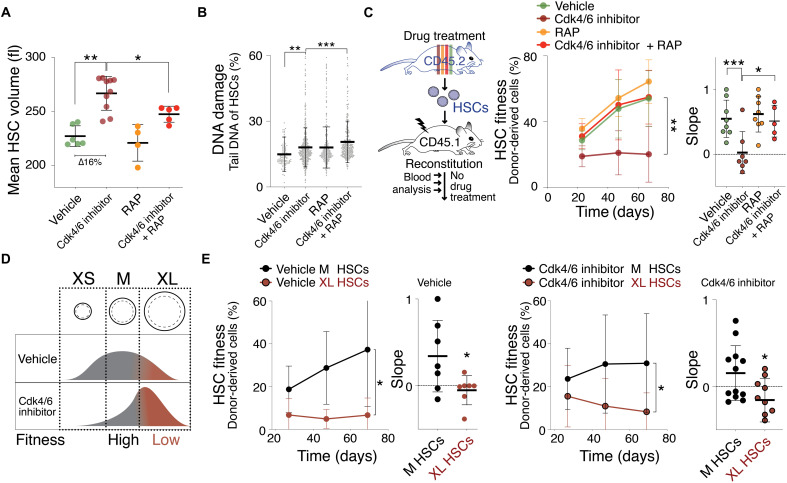
Fig. 2. The Cdk4/6 inhibitor PD enlarges HSCs, causing their decline in reconstitution potential.
(A) Mean volume (fl) of HSCs isolated from mice treated with vehicle (n = 6), Cdk4/6 inhibitor (PD, n = 10), RAP (n = 4), or Cdk4/6 inhibitor + RAP (n = 5) for 85 days (∆ = difference). Same control as in Fig. 1A. (B) DNA damage in CometChip: percentage tail DNA of HSCs (%) isolated from mice treated with vehicle, Cdk4/6 inhibitor (PD), RAP, or Cdk4/6 inhibitor + RAP (n ≥ 552). (C) Reconstitution assay: CD45.2 mice were treated with vehicle (n; donors = 5, recipients = 8), Cdk4/6 inhibitor (PD, n; donors = 5, recipients = 7), RAP (n; donors = 5, recipients = 8), or Cdk4/6 inhibitor + RAP (n; donors = 5, recipients = 5) for 85 days before their HSCs were isolated for transplantation into lethally irradiated CD45.1 recipient mice. No drug treatment was performed after the reconstitution. Percentage (%) of donor-derived white blood cells in recipient and slope of reconstitution kinetics were determined over time. (D) Experimental strategy to determine the role of cell size for HSC fitness: If size determinates fitness, then similarly sized HSCs are expected to exhibit a similar reconstitution potential, irrespective of whether HSCs were treated with vehicle or Cdk4/6 inhibitor (PD). (E) Reconstitution assay: 600 M- or XL-sized HSCs of CD45.2 donor mice treated with vehicle (n; donors = 6, recipients ≥7) or Cdk4/6 inhibitor (PD, n; donors = 9, recipients M = 12, XL = 9) were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipient mice (CD45.1), which were not treated with drugs after the reconstitution. Percentage (%) of donor-derived white blood cells in recipients and slope of reconstitution kinetics were determined over time.