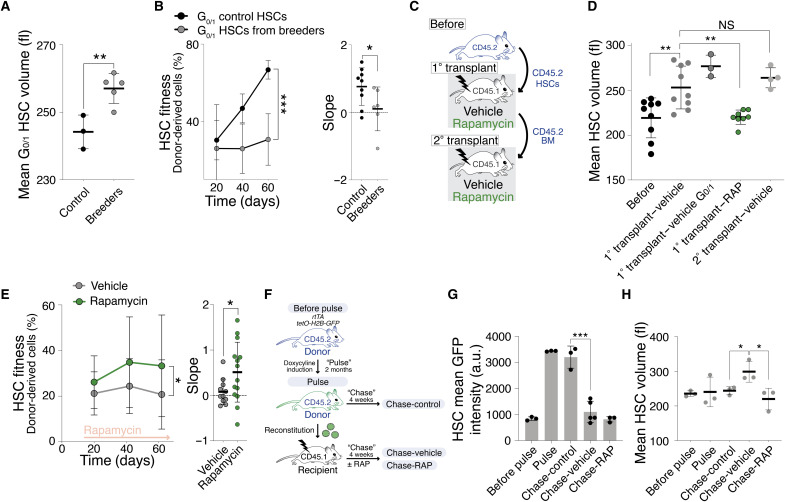
Fig. 4. High cell division frequency enlarges HSCs, contributing to their fitness decline.
(A) Mean volume (fl) of G0/1 HSCs from age-matched virgin (n = 3) and breeding (n = 5) mice. (B) Reconstitution assay: A total of 600 G0/1 HSCs from age-matched virgin (n; donors = 6, recipients = 9) or breeding (n; donors = 5, recipients = 6) donor (CD45.2) mice were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipients. Donor-derived white blood cells (%) in recipients and slope of reconstitution kinetics are shown. (C) Transplantation experiment. (D and E) Following transplantation, recipients were treated with RAP or vehicle. HSC volume was analyzed before transplantation and 80 days after the 1° and 2° transplantation. BM from 1° transplant was used for 2° transplant. (D) Mean volume (fl) of donor HSCs before transplantation (n = 9) and after recipient treatment with vehicle (n = 9), vehicle G0/1 (n = 3), or RAP (n = 8) treatment during 1° or 2° transplantation (n = 4). (E) Reconstitution assay: Donor HSCs were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipients, which were then treated with vehicle (n; donors = 10, recipients = 11) or RAP (n; donors = 10, recipients = 14). Donor-derived white blood cells (%) in recipients and slope of reconstitution kinetics were determined. (F) Experimental overview: rtTa;tetO-H2B-GFP mice (“before pulse”) were treated to induce H2B-GFP (“pulse”). Afterward, HSCs were transplanted into recipients, which were treated with vehicle (“chase-vehicle”) or RAP (“chase-RAP”). Control HSCs from donor rtTa;tetO-H2B-GFP animals were analyzed after the pulse (“chase-control”). (G) Experiment as in (F): GFP intensity (a.u., arbitrary unit) of G0/1 HSCs from before pulse (n = 3), pulse (n = 3), chase-control (n = 3), chase-vehicle (n = 5), and chase-RAP (n = 3) mice. (H) Experiment as in (F): Mean volume (fl) of G0/1 HSCs from before pulse (n = 3), pulse (n = 3), chase-control (n = 3), chase-vehicle (n = 3), and chase-RAP (n = 3) mice.