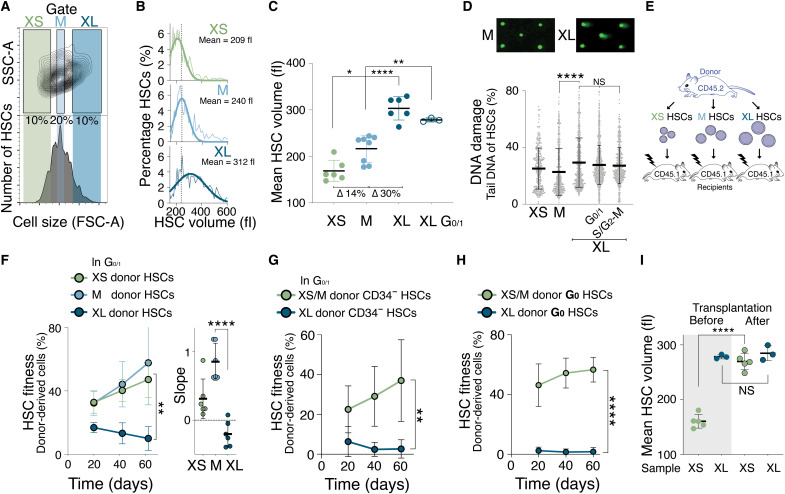
Fig. 5. Naturally large HSCs are impaired in reconstituting the hematopoietic compartment.
(A) Size distribution of HSCs as determined by forward scatter (FSC-A). Gates used to isolate small (XS), medium (M), and large (XL) HSCs are indicated. SSC-A, side scatter. (B) HSCs (%) per volume (fl) isolated using the XS, M, or XL gates shown in (A). Gaussian fit was used to determine mean cell volume. Dotted line marks the mean of M-sized HSCs. (C) Mean volume (fl) of HSCs isolated using the XS (n = 6), M (n = 8), XL (n = 6), or G0/1 XL (n = 3) gates (∆ = difference). (D) CometChip assay to measure DNA damage: Percentage tail DNA of XS-, M- and XL-, G0/1 XL- and S/G2-M XL-sized HSCs (n > 323 cells measured per condition). (E) Schematic of reconstitution experiments in (F) to (H): A total of 600 differently sized donor-derived HSCs were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipients. (F) Reconstitution assay: Donor-derived (CD45.2) white blood cells (%) in recipients after transplantation of XS (n; donors = 5, recipients = 6), M (n; donors = 5, recipients = 6), or XL (n; donors = 5, recipients n = 6) G0/1 Hoechst-labeled donor HSCs. Slope of reconstitution kinetics is shown. (G) Reconstitution assay: Donor-derived (CD45.2) white blood cells (%) in recipients after transplantation of XS HSCs (n = 6) or XL donor G0/1 CD34− HSCs (n = 6). (H) Reconstitution assay: Donor-derived (CD45.2) white blood cells (%) in recipients after transplantation of XS/M (n; donors = 5, recipients = 5) or XL G0 donor HSCs (n; donors = 5, recipients = 5) from Ki67-RFP mice. (I) Mean volume (fl) of XS- or G0/1 XL-sized CD45.2 HSCs before transplantation and their volume at 80 days after transplantation (n ≥ 3). Before data as in (C) and after as in Fig. 7G.