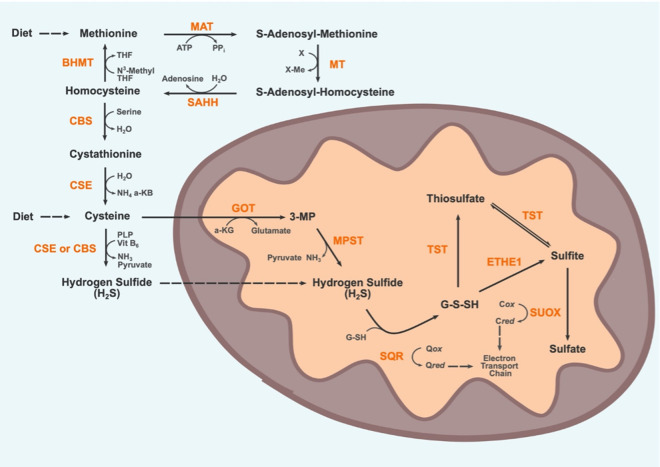
Figure 1. Substrate, intermediates and enzymes involved in the endogenous production and disposal of H2S.
The blue region represents the cytosol, the orange region represents the matrix of a mitochondrion. The transsulfuration pathway cycles methionine into homocysteine first followed by enzymatic conversion of homocysteine into cysteine. From cysteine H2S is generated in the cytosol by CSE and CSE. H2S can also be generated within mitochondria by the action of MPST on 3-MP, a metabolite of cysteine. H2S can freely permeate membranes including the mitochondrial membranes. H2S disposal is carried out in mitochondria by several enzymes that comprise the sulfide oxidation unit (SOU). The precise mechanism of the SOU remains a subject of active research, the species and steps shown here represent just one proposed mechanism. Ultimately H2S is oxidised into sulfate which is subsequently excreted in the urine. MAT, Methionine adenosyl-transferase; ATP, Adenosine triphosphate; PPi, Inorganic pyrophosphate; X, Methyl group acceptor; MT, Methyltransferase; SAHH, S-adenosyl homocysteine hydrolase; BHMT, Betaine-Homocysteine S-methyltransferase; N3-Methyl THF, Trimethylglycine betaine; THF, Betaine; CBS, Cystathionine-β-synthase; CSE, Cystathionine-γ-lyase; NH3, Amine; a-KB, alpha ketobutyrate; PLP, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate; Vit B6, Vitamin B6; GOT, Glutamic-Oxaloacetic Transaminase; a-KG, alpha ketoglutarate; 3-MP, 3-Mercaptopyruvate; MPST, 3-Mercaptopyruvate Sulfurtransferase; SQR, Sulfur-Quinone oxidoreductase; Qox, Oxidised coenzyme Q; Qred, Reduced coenzyme Q; G-S-SH, Glutathione persulfide; ETHE1, Ethylmalonic encephalopathy 1 protein; TST, Thiosulfate Sulfurtransferase; SUOX, Sulfite Oxidase; Cox, Oxidised cytochrome C; Cred, Reduced cytochrome C.