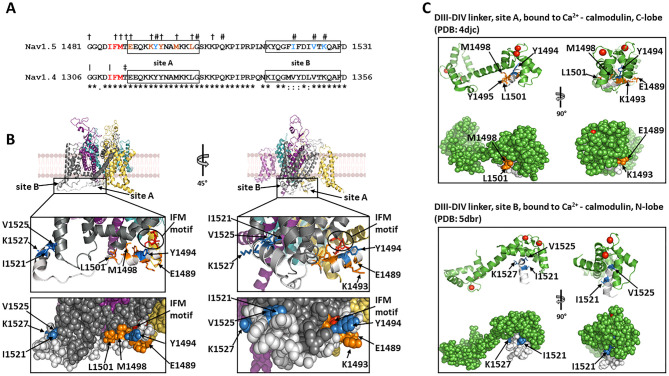
Figure 2. The intracellular DIII-DIV linker.
(A) Sequence alignment of the DIII-DIV linkers from Nav1.5 and Nav1.4. Identical residues indicated by (*), conservative changes by (:) and semi-conservative changes by (.) below the sequence alignments. IFM motifs indicated in red. Site A and site B helices boxed. In the Nav1.5 sequence, examples of residues whose mutations are associated with Long QT syndrome (LQT3) indicated by (†) and with Brugada syndrome (BrS) by (#). LQT3 and BrS-associated residues implicated in binding of the DIII-DIV linker to the α-subunit and to Ca2+-calmodulin coloured orange and sky blue, respectively. In the Nav1.4 sequence, residues whose mutations are associated with myotonia indicated by (|) and with paramyotonia congenita (PMC) by (‡). (B) Expanded view of the Nav1.5 DIII-DIV linker (light grey), showing locations of the key residues coloured in (A), see text for details. (C). Binding of site A helix and site B helix to Ca2+-calmodulin C-lobe and N-lobe, respectively. Note the location of key site A and B residues coloured as in (A) and (B).