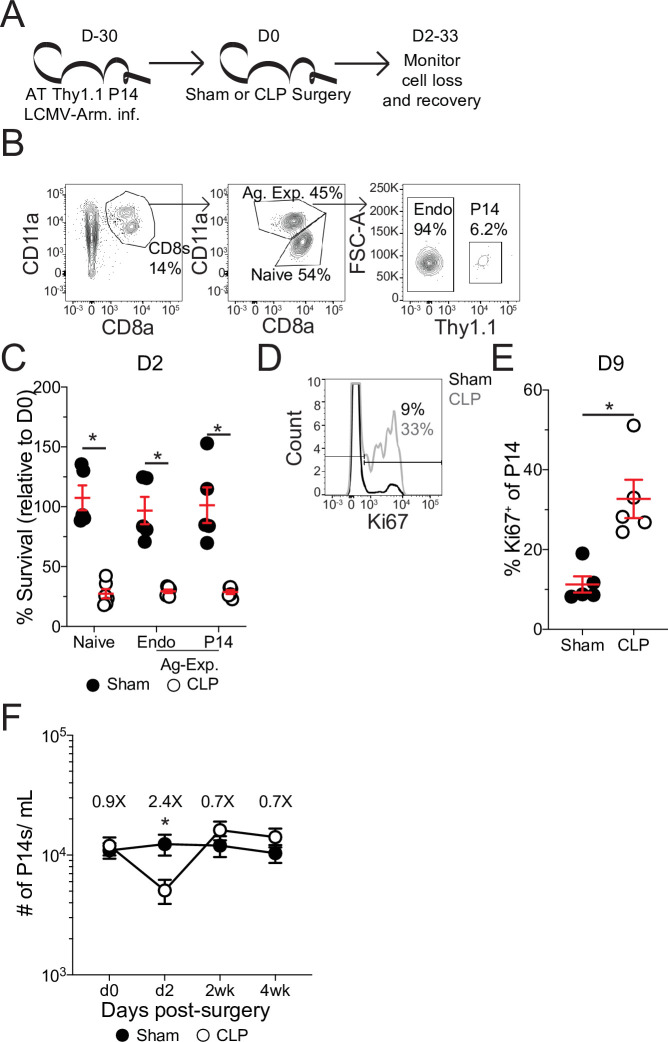
Figure 2. Pre-existing memory CD8 T cells numerically recover with time after sepsis.
(A) Experimental Design: Antigen-experienced P14 chimeric mice were generated by adoptive transfer of 5 × 103 naïve Thy1.1+ TCR-transgenic P14 CD8 T cells to Thy1.2+ C57Bl/6 mice that were subsequently infected with LCMV-Armstrong (LCMV-Arm). Mice underwent Sham or CLP surgery 30 days after infection. The number of endogenous naïve, endogenous antigen-experienced, and antigen-experienced P14 CD8 T cells was monitored in the blood. (B) Representative gating for endogenous naïve, endogenous antigen-experienced, and antigen-experienced P14 CD8 T cells. (C) Percent survival of endogenous naïve, endogenous antigen-experienced, and antigen-experienced P14 CD8 T cells in the blood 2 days after either Sham or CLP surgery, relative to a pre-surgery bleed. (D) Representative gating of Ki67 on P14 CD8 T cells. (E) Frequency of Ki67-expressing P14 CD8 T cells in the blood of Sham and CLP hosts 9 days post-surgery. (F) The number of P14 CD8 T cells per mL of blood in Sham and CLP hosts prior to (d0), or 2 days (d2), 2 weeks (2 wk), and 4 weeks (4 wk) after surgery. Values above the bars indicate the fold difference (Sham/CLP) in the number of P14 CD8 T cells. (C–E) Are representative of 3 independent experiments with 5–6 mice per group. (F) Is cumulative from two independent experiments with 10–12 mice per group. *=p < 0.05. Error bars represent standard error of the mean.