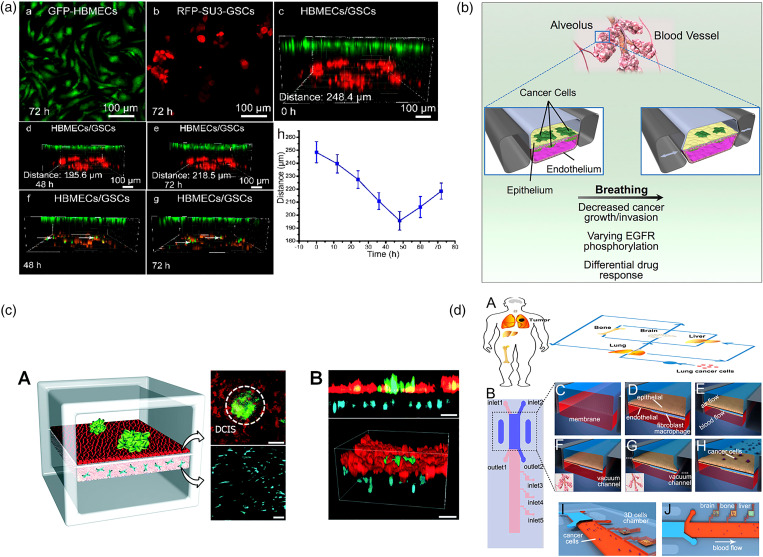
FIG. 7.
Endothelium monolayer–tumor interaction. (a) A biomimetic glioma perivascular niche model on-a-chip. Glioma cancer cells and endothelial cells are planted on the upper and lower sides of a PC membrane, respectively.139 Reprinted with permission from Lin et al., Anal. Chem. 90, 10326 (2018). Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society. (b) A microfluidic human orthotopic lung cancer-on-a-chip model. The endothelium monolayer covers the four walls of the lower channel to mimic the vessel tube. Epithelium and cancer cell aggregates are located on the top surface of the membrane.140 Reprinted with permission from Hassell et al., Cell Rep. 21, 508 (2017). Copyright 2017 Elsevier B.V. (c) A basement membrane based microfluidic model to mimic early-stage cancerous tissue. The breast cancer spheroids are planted on the top of epithelium tissue monolayer.141 Reprinted with permission from Choi et al., Lab Chip 15, 3350 (2015). Copyright 2015 The Royal Society of Chemistry. (d) A bilayer device to study the cancer metastasis. Cancer cells flow through the channel within the artificial blood and get trapped on the epithelium monolayer.142 Reprinted with permission from Xu et al., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 25840 (2016). Copyright 2016 American Chemical Society.