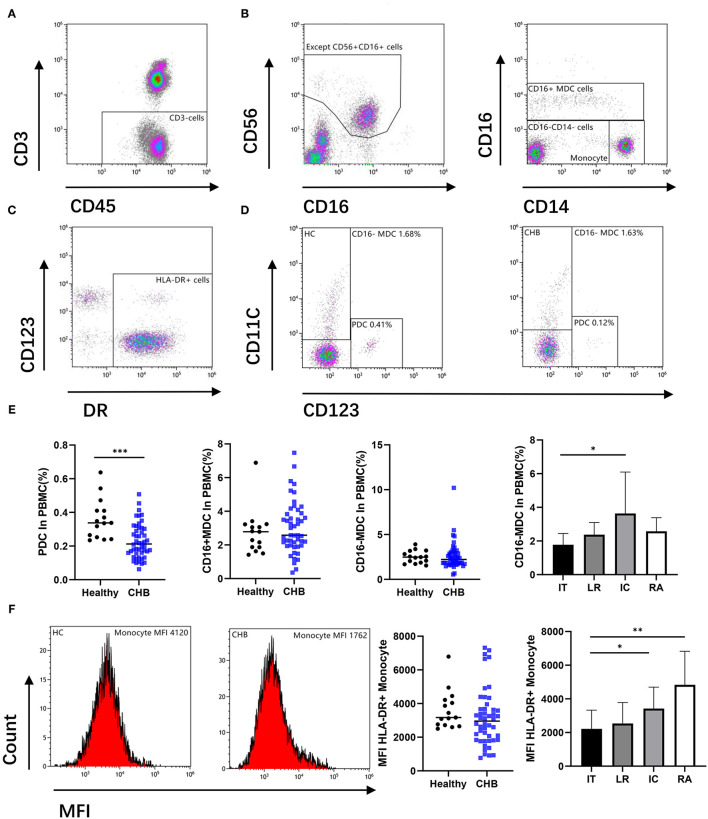
Figure 1.
Antigen-presenting cells (APCs) were altered during chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. (A,B) Remove the CD56 positive cell from the CD3 negative gate, and the remaining parts were divided into CD16+ myeloid dendritic cell (MDC), Monocyte, and CD16–CD14– cell. (C,D) Circle the DR positive cells from CD16 and CD14 double negative cells, there are CD123+ (plasma dendritic cell, PDC) and CD11c+ (CD16– MDC) cells among them. Representative flow cytometry plot indicates the percent frequencies of PDC as well as CD16– MDC in healthy (n = 15) and CHB patients (n = 48) respectively. (E) According to different alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and HBV DNA levels, all chronic hepatitis B (CHB) were divided into immune tolerant (IT; n = 13), lower replicative (LR; n = 13), immune clearance (IC; n = 12) and reactivation (RA; n = 10). The percentages of PDC and MDC in different groups were compared. (F) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of DR in CD14+CD16– Monocyte cell was compared. Each data point represents an individual subject. Horizontal lines show the median. Statistically significant differences are indicated by *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.