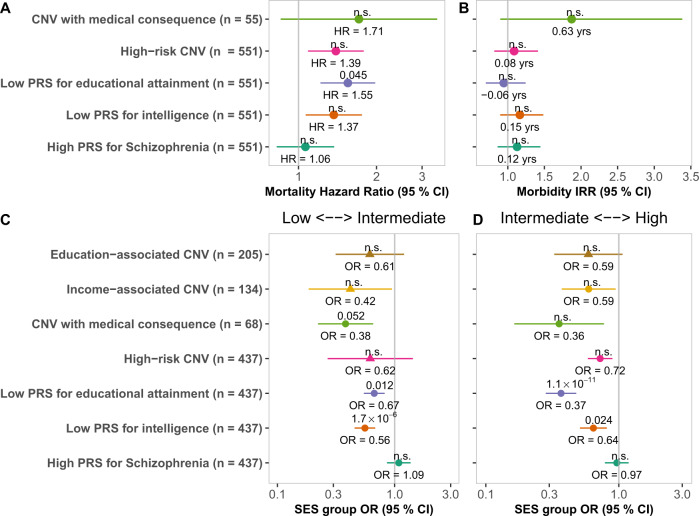
Fig. 3. Health impact of high-risk CNVs and PRSs in Finnish cohorts.
A Hazard ratios in a Cox regression model for mortality in unaffected carriers of high-risk CNVs and individuals at the PRS extremes in FINRISK (n = 22,210). ID gene deletions are not pictured as there were no deaths during follow-up for carriers of this type of CNV. B Incidence rate ratio (IRR) of high-risk CNVs and PRS extremes in a Poisson regression model of the Charlson comorbidity index in FINRISK individuals with no SNPD (n = 22,210). The incidence of one CCI unit was more than 3.5 higher in ID gene deletion carriers than in individuals with no high-risk CNV. C, D Impact of CNVs and PRS outlier status on socioeconomic status and health. The odds of low SES and poor health were highest for individuals with low PRSIQ, and to a lesser extent for individuals at the lowest extreme of PRSEA (A). The odds of high SES and good health was lowest for individuals at the lowest extreme of PRSEA, and to a lesser extent for individuals at the lowest extreme of PRSIQ (B). Effects meta-analyzed using a random-effects assumption are denoted by triangles, otherwise, a fixed-effect assumption was made. The Bonferroni-adjusted p-value is denoted above the point estimate of each variant.