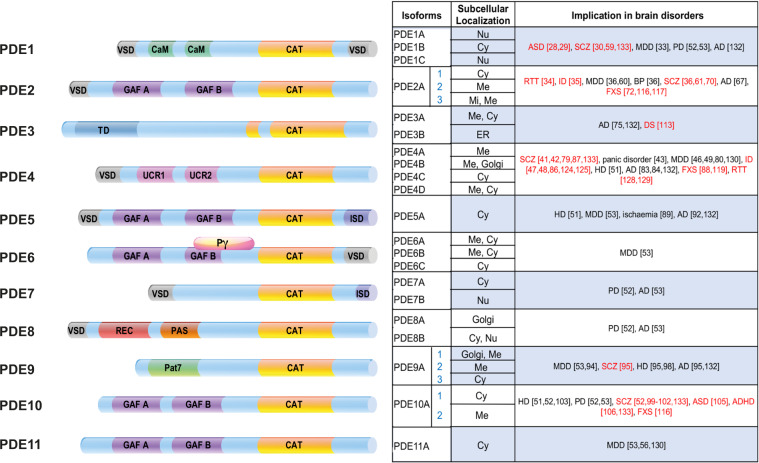
Fig. 2. Structure, localization and implication of PDEs in brain disorders.
Left panel. The structure of each PDE subfamily is indicated by representing the various domains. Catalytic domain providing the substrate specificity: CAT. Regulatory domains: GAF: the name is related to the proteins it is found in: cGMP-specific phosphodiesterases, adenylyl cyclases and the bacterial transcription factor FhlA. Ca2+CaM Ca2+/calmodulin binding site; PAS Per-ARNT-Sim domain, that is a structural motif. TD transmembrane domain. REC cheY-homologous receiver domain. UCR upstream conserved region. ISD isoform specific domain. Regions that are submitted to alternative splicing have been indicated as VSD variant-specific domain. This domain is called PAT7 in PDE9A variants [148] Pγ is part of the PDE6 holoenzyme in rod. Isoforms originated by different genes exist and are indicated for the following subfamily: PDE1 (A, B, and C), PDE3 (A and B), PDE4 (A, B, C and D), PDE6 (A, B and C), PDE7 (A and B) and PDE8 (A and B). PDE2, PDE5, PDE9, PDE10 and PDE11 subfamilies are represented by only one member, namely PDE2A, PDE5A, PD9A, PDE10A and PDE11A. Splicing variants (in blue) of the same protein are indicated when they determine a specific subcellular localization. Middle panel. Localization of each isoform and variant is indicated [4, 6, 148]. Cy Cytosol, Me membrane; Mi mitochondria; Nu Nucleus. Right panel. Brain disorders involving the various PDEs are indicated according to all the genetic and pharmacological information considered in the text. Neurodevelopmental disorders are highlighted in red. AD Alzheimer disease; ASD autism spectrum disorder; BP bipolar disorder; DS down syndrome; HD Huntington disease; ID intellectual disability; FXS fragile X syndrome; MDD major depression disorder, RTT Rett syndrome, SCZ schizophrenia.