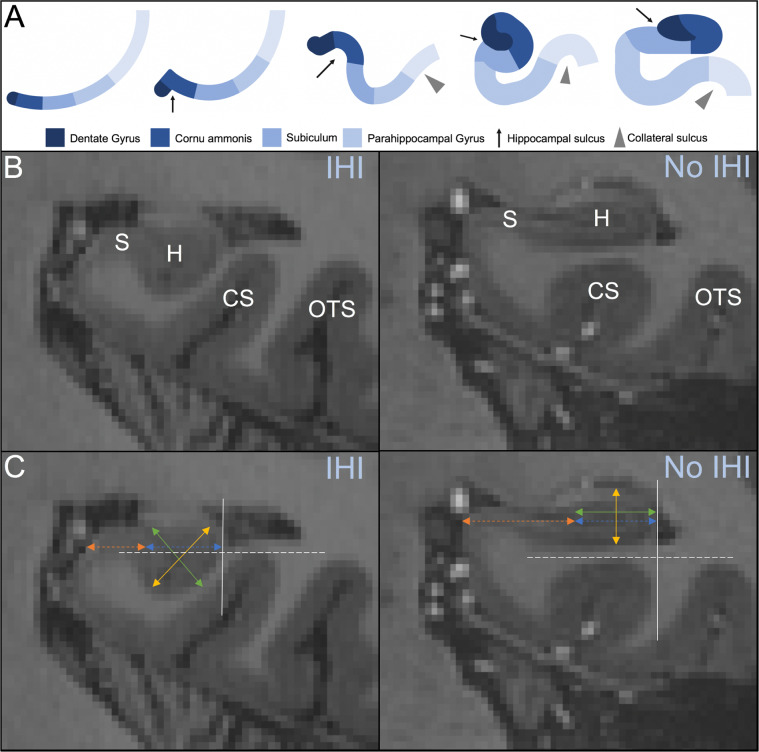
Fig. 1. Incomplete hippocampal inversion.
A Developmental process of the hippocampus from one layer of cortical mantle through early inversion (rounded, verticalized hippocampus with deep collateral sulcus) and late inversion (flat, horizontal hippocampus with shallow collateral sulcus). Arrest in hippocampal development (at Step 4) results in IHI. B 7 T MRI coronal view of an incomplete (left) and complete (right) hippocampal inversion. The hippocampus (H), subiculum (S), collateral sulcus (CS), and occipitotemporal sulcus (OTS) are used as anatomical landmarks to identify IHI. C Criterion 1 is evaluated by comparing the width of the hippocampus (green, solid line) with the height of the hippocampal body (yellow, solid line). The gray, solid line indicates the lateral limit of the hippocampus, which is used for criterion 2. Criterion 3 is measured by comparing the length of the subiculum not covered by the dentate gyrus (orange, dotted line) with the ventral part of the cornu ammonis/subiculum that is covered by the dentate gyrus (blue, dotted line). Criterion 4 is measured using the thickness of the subiculum. The gray, dotted line located at the deepest portion of the CS or OTS is used to evaluate criterion 5.