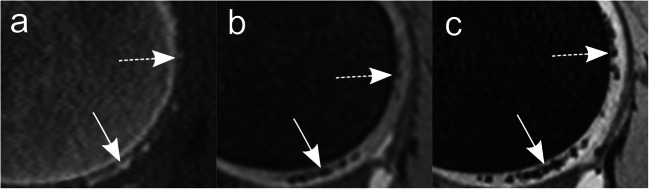
Fig. 4.
Difference in sharpness of chondral calcifications is illustrated on corresponding sagittal CT (a), 3-T MRI (b), and 7-T MRI (c) images of a 52-year-old woman depicting the posterior part of the right lateral femoral condyle. “Very fuzzy” CaCs are shown in the upper part of the femoral condyle as slight hyperdensities in CT (a) and slight hypointensities in 3-T MRI (b) compared to the “fairly sharp” circumscription of the corresponding clear-marked hypointensities in 7-T MRI (c) (dashed arrows). “Fairly sharp” confluent CaCs in the inferior part of the femoral condyle are shown in CT (a) and 3-T MRI (b), compared to a “very sharp” CaC distinction at 7-T MRI (c) (arrows). CaC = calcium crystals, DESS = dual-echo steady state