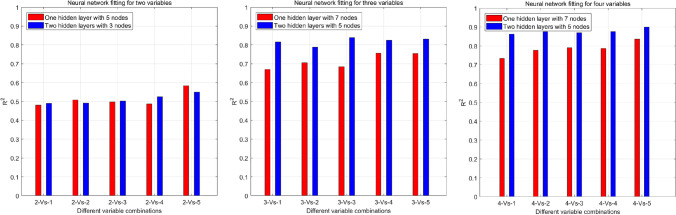
Fig. 3.
a Neural network fitting for two variables. X-axis: 2-vs-1: ICL size, STS; 2-vs-2: ICL size, WTW; 2-vs-3: ICL size, ACD; 2-vs-4: ICL size, LT; 2-vs-5: ICL size, ATA. R2 values are presented on the y-axis. Red and blue bars represent the model containing one hidden layer with five nodes and two hidden layers with three nodes in each layer, respectively. b Neural network fitting for three variables. X-axis: 3-vs-1: ICL size, ACD, WTW; 3-vs-2: ICL size, ATA, WTW; 3-vs-3: ICL size, ACD, LT; 3-vs-4: ICL size, ATA, LT; 3-vs-5: ICL size, ATA, ACD. R2 values are presented on the y-axis. Red and blue bars represent the model with one hidden layer and seven nodes and the model with two hidden layers and five nodes in each layer, respectively. c Neural network fitting for four variables. X-axis: 4-vs-1: ICL size, ATA, WTW, STS; 4-vs-2: ICL size, ACD, ATA, WTW; 4-vs-3: ICL size, ATA, LT, WTW; 4-vs-4: ICL size, ACD, LT, WTW; 4-vs-5: ICL size, ACD, ATA, LT. R2 values are presented on the y-axis. Red and blue bars represent the model with one hidden layer and seven nodes and the model with two hidden layers and five nodes in each layer, respectively. WTW, white-to-white; ACD, anterior chamber depth; ATA, angle-to-angle; STS, sulcus-to-sulcus; LT, lens thickness; ICL, implantable collamer lens