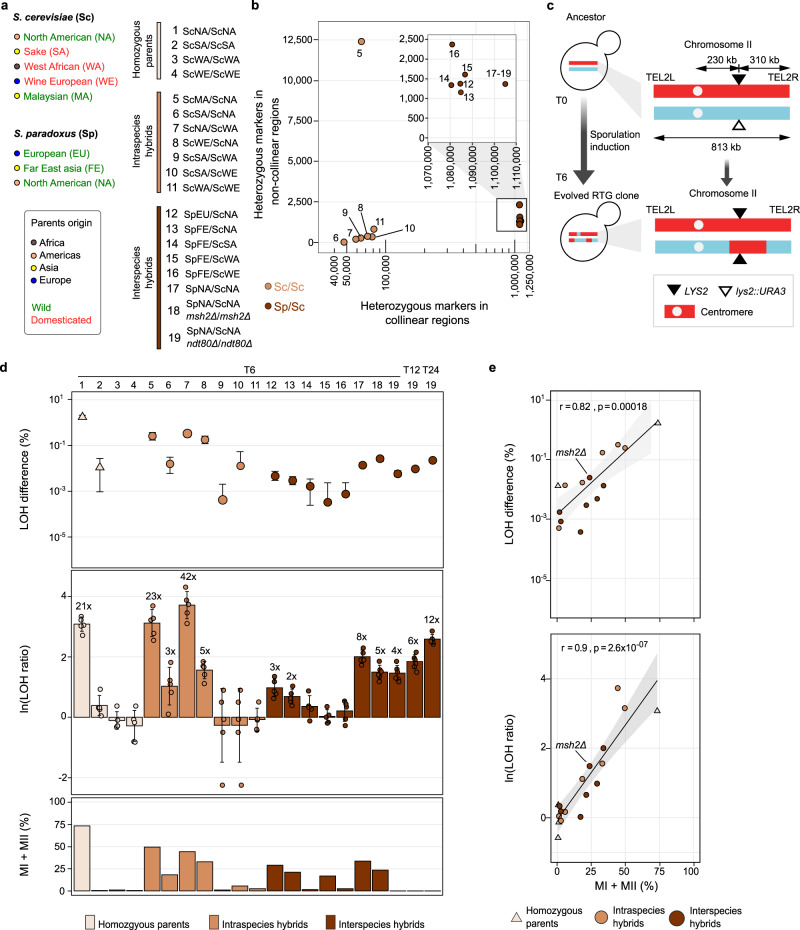
Fig. 2. Quantifying RTG-induced recombination across hybrid diversity.
a Geographical (coloured circle) and ecological (coloured name) origins of the parental strains (left) used for generating the diploid backgrounds (right). Diploids are grouped according to their level of heterozygosity as: homozygous parents (light brown), intraspecies hybrids (brown) and interspecies hybrids (dark brown) and the same colour codes apply to b, d and e. b Level of heterozygosity across the hybrid panel with the number of markers detected in non-collinear and collinear regions. Each data point is labelled with a number/colour encoded according to a. The four homozygous parents are not reported. c URA3-loss assay used for measuring RTG-induced recombination rates. d Top: the y axis reports in logarithmic scale the percentage of cells growing in 5-FOA measured with the URA3-loss assay and quantified with the LOH difference (RT6−RT0) where RT6 and RT0 are the LOH rates at T6 and T0, respectively (Supplementary notes). Error bars represent standard deviations. Each point represents the average of n = 5 independent replicates. Samples having a negative LOH difference (non-significant differences between control and RTG sample) are not reported. Middle: cell growth quantified with the natural logarithm of the LOH ratio (RT6/RT0). Error bars represent standard deviations. Each point represents the average of n = 5 independent replicates. The number on the top of each bar indicates the linear fold increase. Bottom: meiotic progression after 12 h measured as the percentage of cells that passed the first (MI) and the second (MII) meiotic divisions (quantified with fluorescence microscopy of DAPI-stained cells). e Correlation between the meiotic progression (MI + MII cells after 12 h in sporulation medium) and the LOH difference (top, logarithmic scale) as well as the natural logarithm of the LOH ratio (bottom). r is the Pearson’s correlation coefficient, the p value of the correlation is calculated as a two-sided test. In both plots, the grey area represents the 95% confidence interval. Samples showing negative LOH differences were removed to avoid a bias towards correlation.