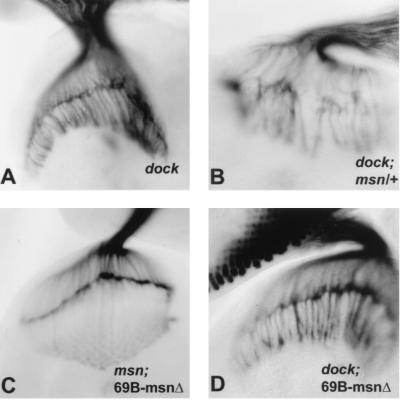
FIG. 3.
Genetic interaction between msn and dockP1. All panels show third-instar larval eye-brain complexes stained with 24B10. (A) dockP1. (B) dockP1; msn102/+. msn enhances the dock phenotype. Twenty-two eye-brain complexes homozygous for dock and heterozygous for msn were compared to 14 complexes homozygous for dock, and a consistent enhancement was seen in all samples. (C) msn102, 69B-GAL4/msn102, UAS-msn(Δ332–667). (D) dockP1; elav-GAL4/UAS-msn(Δ332–667). UAS-msn(Δ332–667) rescues both the defect in dorsal closure (Table 1) and the defect in photoreceptor axonal targeting in msn mutants (C). However, expression of UAS-msn(Δ332–667) fails to rescue photoreceptor axonal targeting in dockP1 mutant third-instar larvae (D).