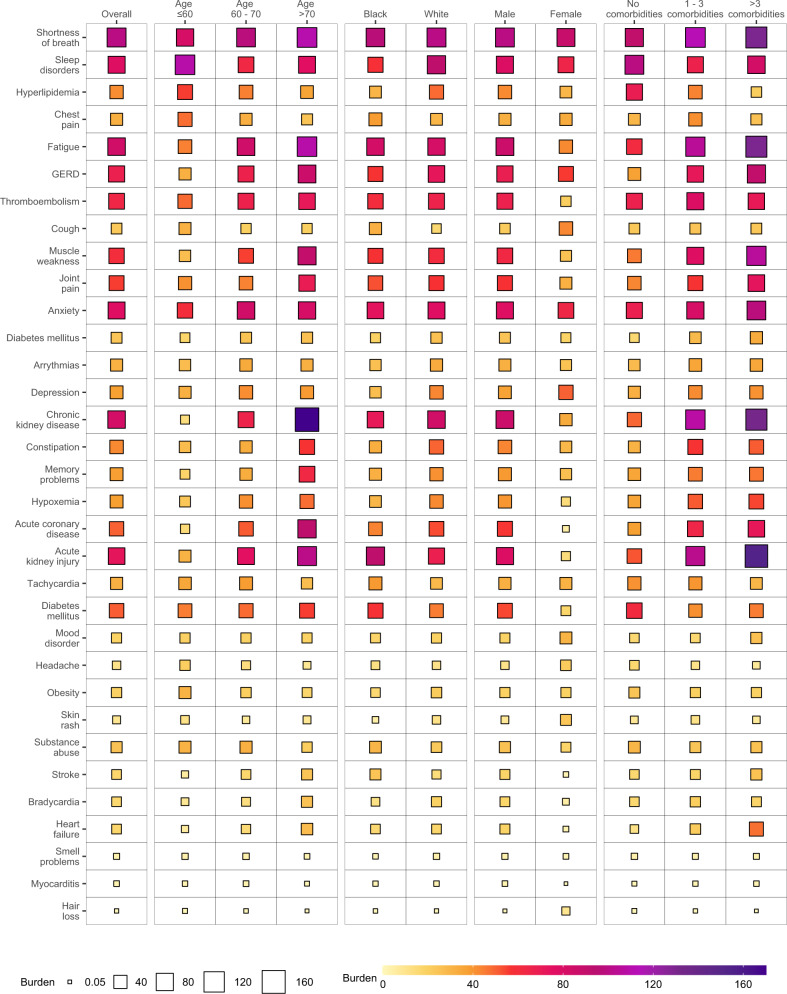
Fig. 7. Burden of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19 in the overall cohort and by age, race, sex, and health status in COVID-19 patients admitted to intensive care.
Estimates of burdens per 1000 COVID-19 patients at 6 months are presented. The size of the square represents the burden within each care setting. The intensity of color from light yellow to deep purple represents the range of burdens across care settings. Models adjusted for age, race, sex, receipt of long-term care, Area Deprivation Index, number of outpatient encounters, number of hospital admissions, number of outpatient prescriptions, number of outpatient serum creatinine measurements, chronic lung disease, cancer, cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, dementia, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, depression, anxiety, chronic kidney disease, hepatitis C and peripheral artery disease, overweight, obesity, smoking status, Charlson Comorbidity Index, US geographic region, total number of beds, number of COVID-19 tests administered, COVID-19 positivity rate, and average hospital bed occupancy during the week of participant enrollment when appropriated.