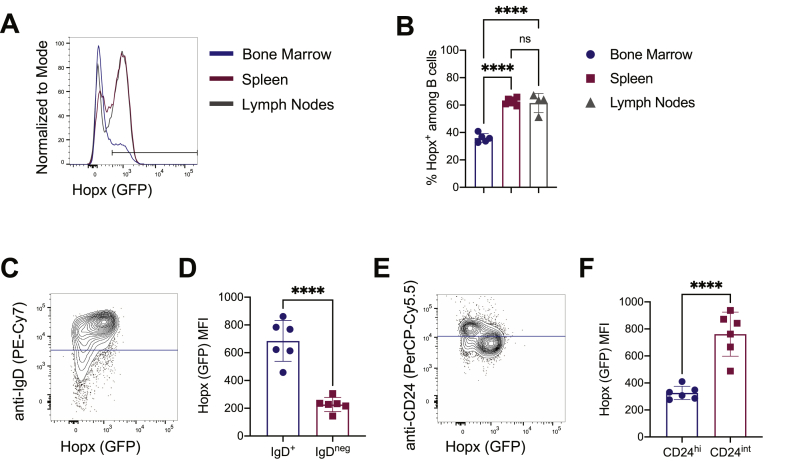
Figure 3.
Hopx is expressed in naïve B cells. Cells from bone marrow, spleens, and peripheral lymph nodes of HopxGFPFoxp3RFP mice were analyzed by flow cytometry. (A) Representative overlaid histograms show Hopx (GFP) expression among B cells (gated as single, live, CD19+, B220+) from the bone marrow (blue), spleen (red), or peripheral lymph nodes (gray). (B) Graph shows the percentages of Hopx+ cells among B cells from bone marrow, spleens, and peripheral lymph nodes as indicated (n = 4–6 mice from three independent experiments). (C) Representative plot shows Hopx (GFP) expression and anti-IgD staining intensity among splenic B cells. The blue line indicates the cutoff for IgD+ and IgDneg cells further analyzed in D. (D) Graph shows median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Hopx (GFP) expression among splenic IgD+ and IgDneg B cells as indicated (n = 6 mice from three independent experiments). (E) Representative plot shows Hopx (GFP) expression and anti-CD24 staining intensity among splenic B cells. The blue line indicates the cutoff for CD24hi and CD24int cells further analyzed in F. (F) Graph shows median fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Hopx (GFP) expression among splenic CD24hi and CD24int B cells as indicated (n = 6 mice from three independent experiments). (B, D, and F) Graphs show mean ± SD. ns – not significant and ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001 determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons (B) or unpaired two-tailed t test (D and F).