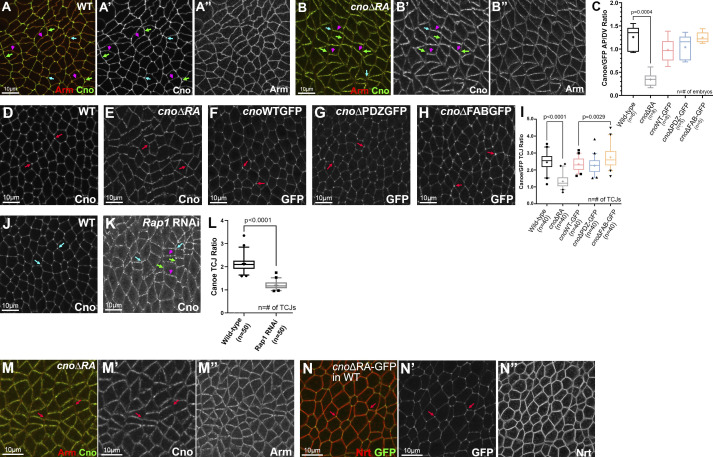
Figure 3.
The RA domains are important for enrichment at junctions under tension, while the PDZ and FAB domains are dispensable. Stage 7. (A) WT Cno is enriched at TCJs (cyan arrows) and at AP borders (green arrows) versus DV borders (magenta arrows). (B) In contrast, CnoΔRA is strongly enriched at DV borders (magenta vs. green arrows). TCJ enrichment is lost (cyan arrows). (C) Quantification of CnoΔRA planar polarity. Brown Forsythe and Welch ANOVA statistical test, and n indicates the number of embryos analyzed. (D–H) WT Cno, CnoWT, CnoΔPDZ, and CnoΔFAB all are enriched at TCJs (arrows). CnoΔRA TCJ enrichment is substantially reduced. (I) Quantification of TCJ ratio (Brown Forsythe and Welch ANOVA statistical test, and n indicates the number of TCJ analyzed). (J–L) Rap1 is required for TCJ enrichment of WT Cno (K, cyan arrows, quantified in L), and its knockdown also reverses Cno planar polarity (K, magenta vs. green arrows). (L) Quantification of Cno planar polarity after Rap1 RNAi. Unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (two-tailed P value) statistical test, and n indicates the number of TCJs analyzed. (M and N) While CnoΔRA enrichment at TCJs (arrows) is lost when it is expressed alone (M’), this is restored if it is expressed in a WT embryo along with WT Cno (N’). (C, I, and L) The boxes show the 25th–75th percentiles, the whiskers are 5th–95th percentiles, the horizontal lines are the median, and the plus signs (+) are the mean.