Figure 5.
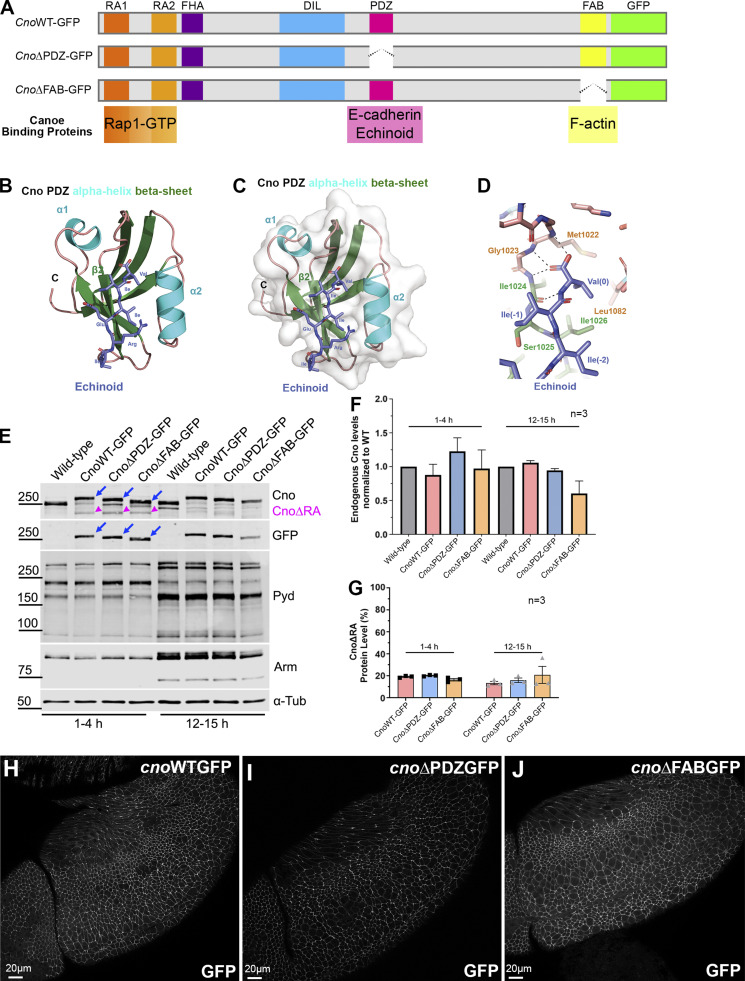
Defining Cno’s PDZ domain structure and generating mutants deleting it or the FAB domain. (A) Cno protein domains, CnoΔPDZ and CnoΔFAB. (B) Ribbon diagram, Cno PDZ (green, β-strands; cyan, α-helices; teal, loops) bound to Ed’s C-terminal peptide (purple; IREIIV-COOH). (C) Surface structure. (D) Zoom view. Cno PDZ–Ed binding site. Key hydrophobic residues in binding pocket form van der Waals contacts with Ed and backbone determinants in the binding groove form hydrogen bonds (black dashed lines) with Ed’s terminal valine. (E) Mutants are expressed at WT levels. Immunoblot, embryonic extracts. α-Tubulin was used as a loading control. Blue arrows, full-length mutant proteins; magenta arrowheads, truncated CnoΔRA. (F) Protein levels relative to WT. (G) Levels of residual CnoΔRA. (F and G) Error bars represent SEM, and n indicates the number of independent replicates. (H–J) Stage 9. CnoΔFAB and CnoΔPDZ AJ localization is unchanged.