Figure 9.
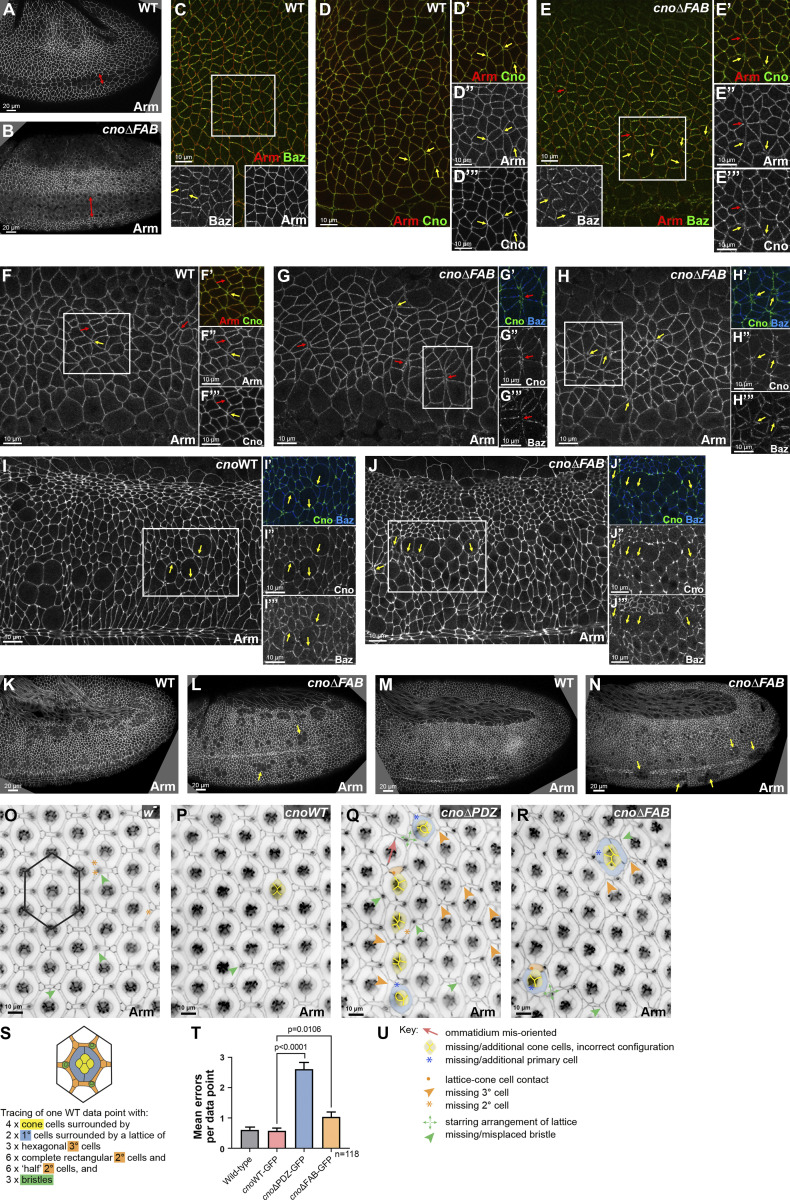
Deleting the FAB domain leads to defects in mesoderm invagination and at AJs under tension. (A and B) Stage 8. cnoΔFAB has impaired mesoderm invagination (double-headed arrow). (C–E) Stage 7. WT Arm and Cno extend to TCJs (D, yellow arrows). Baz is planar polarized (C, inset, arrows). (E) cnoΔFAB. Small gaps (E–E″′, red arrow) or fragmented TCJs (yellow arrows). Accentuated Baz planar polarity with loss from AP borders (E, inset, yellow arrows). (F–H) Stage 8. WT Arm and Cno are continuous at shrinking AP borders (F, red arrows) and TCJs (F, yellow arrow). (G and H) cnoΔFAB. Gaps at TCJs (G and H, yellow arrows) and along AP borders of aligned cells (F vs. G, red arrows). Baz lost along AP borders (G″′). (I and J) Stage 9. cnoΔFAB. Modest defects in AJs remain near mitotic cells (I vs. J, arrows). (K and L) Stage 10. (M and N) Stage 11. cnoΔFAB. Cells along the ventral midline delayed in resuming columnar architecture (L, arrows) or with reduced epithelial integrity (N, arrows). (O–R) Small regions of control w- (O), cnoWT (P), cnoΔPDZ (Q) and cnoΔFAB (R) retinas dissected at 40 h after puparium formation. (U) Examples of patterning errors are illustrated as per key. Patterning errors were scored in hexagonal data points as superimposed on O and illustrated in S, with epithelial cell types listed as per color-code. (T) Mean numbers of patterning errors per genotype. Error bars represent SEM, and n is the number of ommatidia. Unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (two-tailed P value) statistical test.