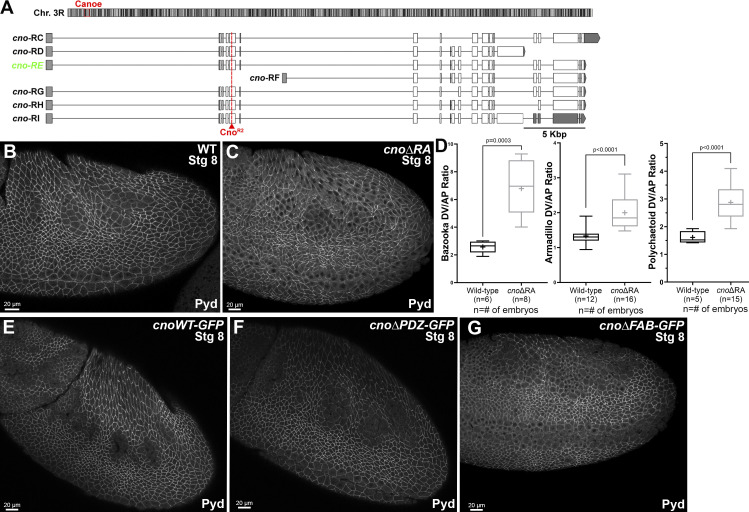
Figure S1.
cno locus and aspects of the phenotypes of cnoΔRA, cnoΔPDZ and cnoΔFAB. (A) Top: Position of cno locus near the base of the right arm of the third chromosome. Bottom: Predicted mRNAs encoding different cno isoforms. Our choice of cno-RE was guided by modEncode and other data available on JBrowse at FlyBase. The predicted internal start site of cno-RF is not supported by modENCODE or RAMPAGE data (J-Browse), and transcription of its unique first exon is not detected in RNA-sequencing data until after 20 h of embryonic development. modENCODE data also suggest the large alternate exon present in cno-RD and cno-RI is transcribed at lower levels than the other exons. cno-RE has the longest coding sequence of the other predicted isoforms. (B and C) Stage 8. The ZO-1 homologue, Pyd, remains localized to AJs in cnoΔRA mutants, though like Arm, its planar polarization to DV borders is increased. (D) Baz, Arm, and Pyd planar polarization are enhanced in cnoΔRA mutants. Unpaired t test with Welch’s correction (two-tailed P value) statistical test, and n is the number of embryos analyzed. The boxes show the 25th–75th percentiles, the whiskers are 5th–95th percentiles, the horizontal lines are the medians, and the plus signs (+) are the mean. (E–G) Stage 8. Pyd localization to AJs appears unchanged in cnoWT, cnoΔPDZ, and cnoΔFAB mutants.