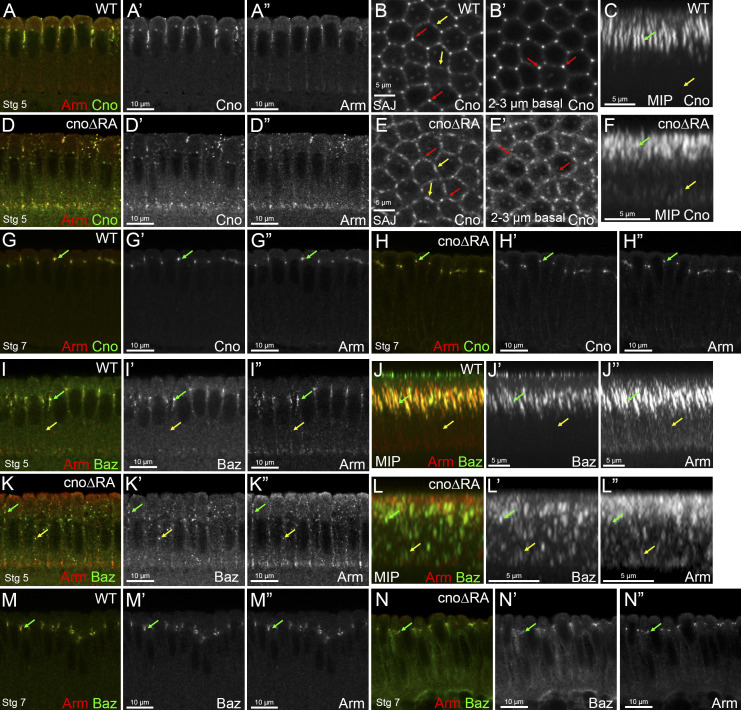
Figure S2.
The RA domains are important for Cno localization and its roles in AJ polarization during cellularization. (A–F and I–L) Stage 5. (G, H, M, and N) Stage 7. (A, D, G–I, K, M, and N) Cross sections. (B and E) En face views. (C, F, J, and L) MIPs of cross sections. (A–H) Embryos stained with Arm and Cno. (I–N) Embryos stained with Arm and Baz. cnoΔRA embryos have defects in Cno’s apical restriction (A and A’ vs. D and D’) with Cno localizing not only apically but also more basally (C vs. F, yellow arrows). cnoΔRA embryos also have defects in Cno’s TCJ enrichment at SAJs vs. bicellular junctions (B vs. E, red arrows vs. yellow arrows). cnoΔRA TCJ enrichment defects are even more striking deeper into the embryo (B’ vs. E’, red arrows). MIPs reveal that lack of the RA domains affects Cno rod-like structure at TCJs (C vs. F, green arrow). Cno localization is restored during stage 7 in cnoΔRA mutant embryos (G vs. H, arrow). cnoΔRA embryos have defects in Baz and Arm localization with puncta localizing both apically (I vs. K, green arrow) and basolaterally (I vs. K, yellow arrow). MIPs reveal that both Baz and Arm localization is scattered along the membrane (J vs. L, yellow arrow), with some apical localization retained (J vs. L, green arrow). This localization defect is restored back to normal during stage 7 (M vs. N, arrow).