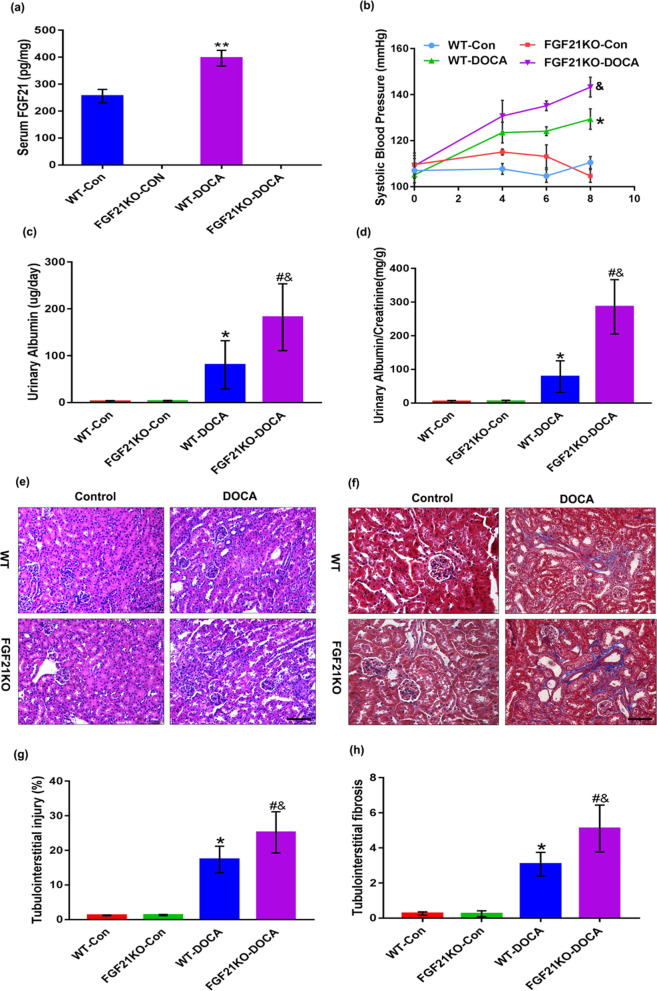
Fig. 2.
FGF21 deficiency enhanced DOCA-salt-induced hypertensive renal damage in mice. Eight-week-old male FGF21 wild type (WT) and FGF21 knockout (KO) mice based on C57BL/6J were treated with DOCA-salt or sham operation as controls. a Serum FGF21 levels in each group were determined by ELISA. b Changes in systolic blood pressure measured by a tail-cuff within 8 days at various time points. c and d Urinary albumin levels and urinary albumin/creatinine ratio were monitored at 8 days in various group mice. e and f Representative images of Hematoxylin–eosin staining and Masson’s trichrome staining in kidney sections harvested at 8d post-DOCA-salt treatment. g Quantification of tubulointerstitial injury region from the Hematoxylin–eosin stained images using Image J software. h Quantification of fibrotic degree in tubulointerstitium from the Masson's trichrome stained images using Image-Pro plus 6.0 software. The values are expressed as the mean ± SD, n = 6 mice/group. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus the WT control group; #P < 0.05 versus the FGF21KO control group; &P < 0.05 versus the WT-DOCA group. Scale bar: 100 μm