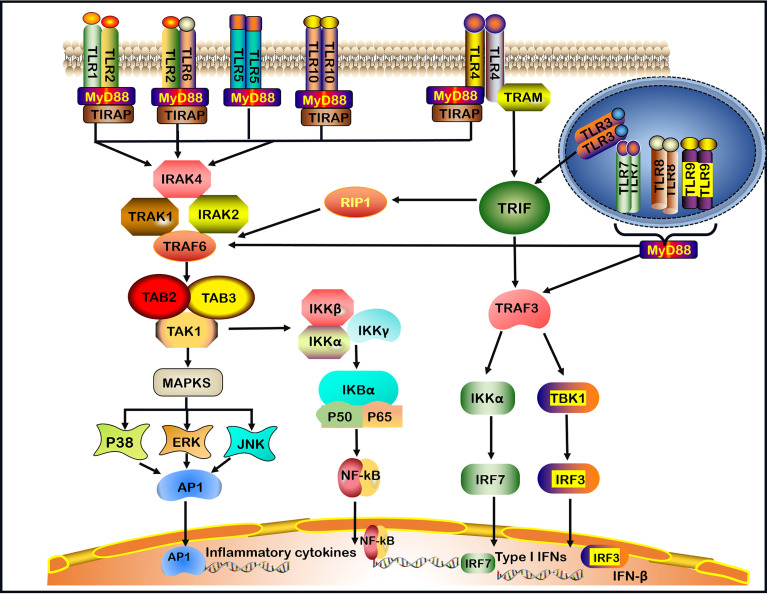
Figure 1.
TLRs signaling pathways. TLRs (Toll-like receptors) recognize invading microbes and activate signaling pathways, which regulate immune and inflammatory responses. TLR1, TLR2, TLR5, TLR6, and TLR10 are located on the cell surface.TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9 are located on the intracellular endosome membranes. All TLRs, with the exception of TLR3, by the (MyD88)- dependent signaling pathway. In addition, TLR4 signaling takes place in both MyD88-dependent and the MyD88-independent signaling pathway. In MyD88-dependent signaling pathway, the leucine-rich repeats (LRR) region of TLR binds to ligands resulting in the formation of TLRs heterodimer, such as TLR2-TLR1/TLR2-TLR6/TLR7-TLR8 heterodimer or TLR4/TLR9 homodimer, which induces the recruitment of the TIR domain-containing adaptor protein (TIRAP)/MyD88/interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 (IRAK-1)/IRAK2/IRAK-4 complex. After that, the complex continues to activate tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and subsequent transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1), TAK1-Binding Protein-1(TAB1) and TAK1-Binding Protein-2(TAB2), leading to the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs, including subsequent activation of P38, ERK, and JNK) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway, and promoting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In the MyD88-independent signaling pathway, the activation of TLR3 or TLR4 can recruit TRIF. In particular, TLR4 requires a TRIF-related adaptor molecule (TRAM) for the activation of TRIF. Then, TRIF activates receptor-interacting protein 1(RIP1) and interacts with TRAF6 to promote subsequent inflammation signaling pathways. In addition, TRIF activates TRAF3, which in turn induces the activation of IRF3 and IRF7 to produce IFN-β and Type I IFNs respectively. Finally, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9 activate TRAF3 or TRAF6 and subsequent signaling pathways through the MyD88-dependent pathway.