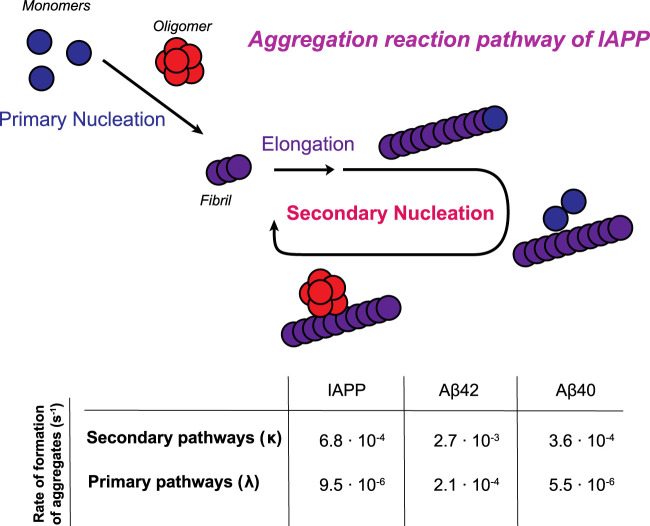
FIGURE 5.
Schematic illustration of the aggregation reaction pathway of IAPP. Monomers initially aggregate through a primary pathway (primary nucleation and elongation). Once a critical amount of fibrils has been formed, the catalytic nature of secondary nucleation becomes the dominant process in generating the oligomers in the aggregation process. In the table, the rates of formation of aggregates through primary and secondary pathways are calculated for a 5 µM sample in 33 mM acetate, 150 mM KCl, pH 5.3. Rate constants of Aβ42 in 20 mM sodium phosphate, pH 8.0 and Aβ40 in 20 mM sodium phosphate, pH 7.4 are obtained from (Cohen et al., 2013; Meisl et al., 2014).