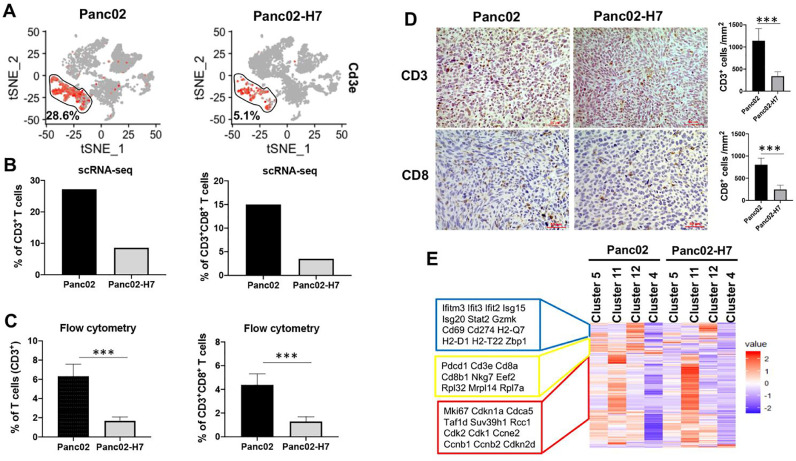
Fig. 3.
Characterization of tumor-infiltrated T cells in Panc02 and Panc02-H7 tumors. (A) Frequency of tumor-infiltrated T cells defined with tSNE plot. The results show the frequency of T cells positive for Cd3e in Panc02 and Panc02-H7 induced PaC tumors. (B) The frequency of total CD3+T cells (Left panel) and CD8 T cells (Right panel) in total viable cells. Based on scRNA-seq data shown in Fig. 2B, CD3+ T cells consist of four cell clusters including T cell 1, T cell 2, T cell 3, and T cell 4; CD8 T cells consist of three cell clusters including T cell 1, T cell 2, and T cell 3. (C) Flow cytometric assay of tumor-infiltrating T cells in two types of tumors. Flow cytometry assay detected significantly higher proportion of both T cells (CD3+) (left panel) and CD8 T cells (CD3+CD8+) (right panel) in Panc02-forned tumors than Panc02-H7-formed tumors. n = 5, *** p < 0.001. (D) IHC staining of tumor-infiltrating CD3+ T cells and effector CD8+ T cells. IHC staining was used to detect CD3+ and CD8+T cells in tumors formed with Panc02 and Panc02-H7 cells. The semi-quantitative assay defines tumor infiltrating CD3+ and CD8+ cells per mm2 field. Scale bars, 50 µm. n = 5, *** p < 0.001. (E) Heat map showing differentially expressed genes in four T cell clusters in Panc02 and Panc02-H7 induced PaC tumors. Only genes were selected if their expressions are different in any pairwise comparison between two tumors or different clusters. Each row represents a gene. Color scheme represents Z-score distribution from −2 (blue) to 2 (red).