-
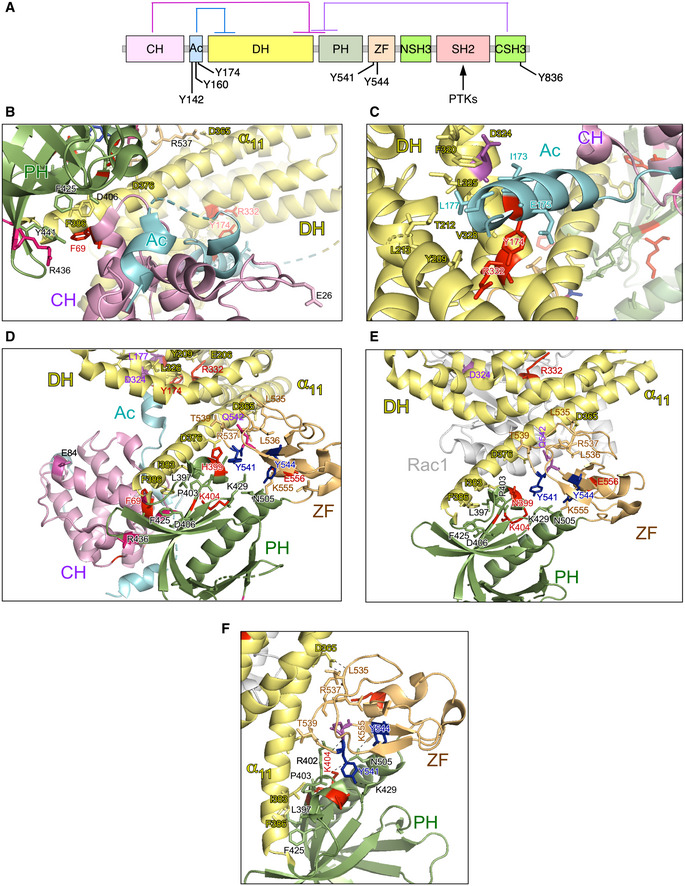
A
Depiction of the main intramolecular interactions that mediate the inactivation of VAV family proteins in the nonphosphorylated state. The interactions of the CH, Ac, and CSH3 domains with the catalytic cassette are shown in pink, blue, and purple lanes, respectively. The phosphorylation sites involved in the activation step are indicated. PTKs, protein tyrosine kinases involved in the tyrosine phosphorylation‐mediated activation step of VAV family proteins.
-
B, C
Depiction of areas of interaction between the CH‐Ac and the catalytic cassette. The side chains of the residues whose mutation leads to GOF effects are shown in red. The main regulatory phosphosites are shown in blue. The CH, Ac, and DH region are colored in purple, blue, and yellow, respectively.
-
D, E
Depiction of the area of the catalytic cassette containing the α11 DH helix, the PH, and the ZF regions in the context of the crystallized CH‐Ac‐DH‐PH‐ZF (D) and the CH‐PH‐ZF (E) fragments of human and mouse Vav1, respectively. Residues whose mutation leads to GOF and LOF effects are colored in red and blue, respectively. The CH, Ac, DH, PH, and ZF regions are colored in purple, blue, yellow, green, and brown, respectively.
-
F
Zoom of the Vav1 α11 DH helix‐PH‐ZF region showing the interactions established by the indicated residues. Residues and domains are depicted as in above panels.