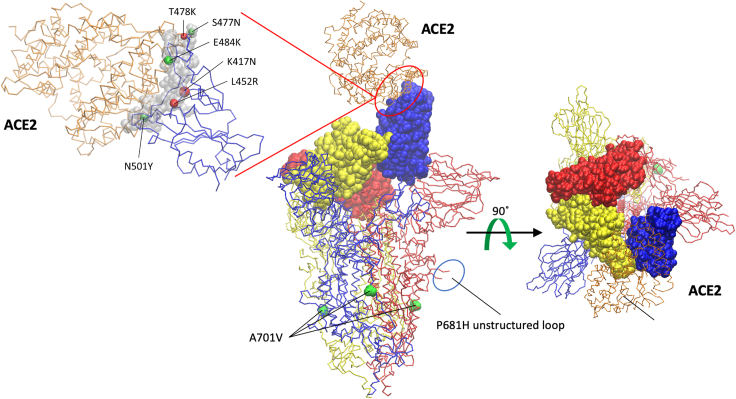
Figure 4.
Mutations identified within SARS-CoV-2 variants mapped into the structure of SARS-CoV-2 spike-ACE2 complex
The structure of the trimeric spike (S) glycoprotein (PDB: 7df4) (Xu et al., 2021) is shown in a trace backbone representation with individual chains differently colored. ACE2 protein is colored in orange. The RBD domains (amino acid [aa] 333–527) of the spike protein are highlighted using a Van der Waals representation. Mutations S477N, T478K, E484K, K417N, L452R, and N501Y are located in the RBD, but only S477N, E484K, and N501Y form direct contacts with ACE2, as revealed by the RBD/ACE2 interface analysis by using the Knowledge-based FADE and Contacts (KFC2) server (Darnell et al., 2007). Although residues K417 T478, and L452 are not part of the RBD/ACE2 interface, mutations at these positions may affect complex stability indirectly by modifying the properties (conformation) of the nearby interface-forming residues.