Fig. 6. L-type Ca2+ channel antagonist, isradipine effects on ICC-MY Ca2+ transients.
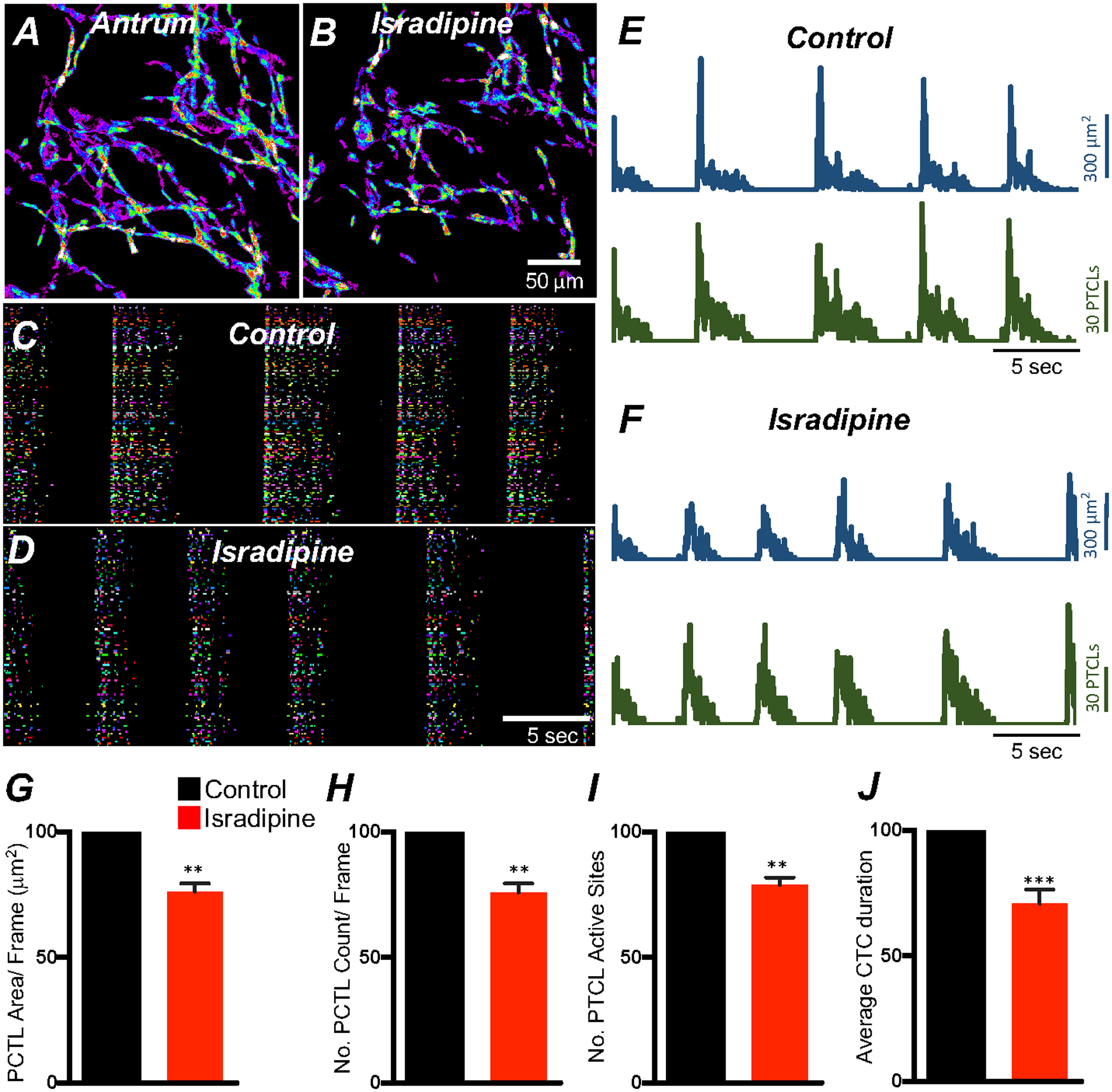
A&B Representative heat-map images of an antrum ICC-MY network showing active Ca2+ PTCLs under control conditions and in the presence of isradipine (1mM). Ca2+ activity is color-coded with warm areas (white, red) representing bright areas of Ca2+ fluorescence and cold colors (purple, black) representing dim areas of Ca2+ fluorescence. Scale bar is 50 mm in both A & B. C & D Ca2+ activity in ICC-MY showing color-coded Firing sites plotted as an occurrence map under control conditions C and in the presence of isradipine (1mM) D. Traces of firing sites showing PTCL area (E; blue) and PTCL count (E; green) under control conditions and in the presence of isradipine; PTCL area (F; blue) and PTCL count (F; green). Summary graphs of Ca2+ PTCL activity in ICC-MY before and in the presence of isradipine are shown in G (PTCL area/frame), H (PTCL count/frame), I the number of PTCL active sites. J Summary graph of Ca2+ transient clusters (CTCs) duration. Data were normalized to controls and expressed as percentages (%). Significance determined using unpaired t-test, ** = P < 0.01, *** = P < 0.001, n = 6. All data graphed as mean ± SEM.
