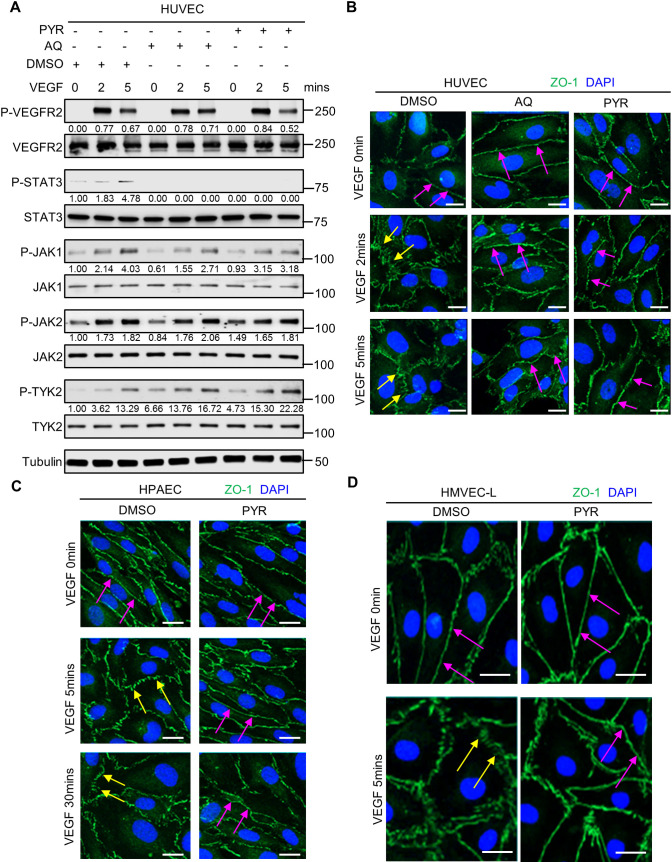
Fig. 3.
Pharmacological inhibition of STAT3 stabilizes endothelial barrier integrity following VEGF stimulation in human endothelial cells. (A) Serum-starved human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were pretreated with DMSO (vehicle control) for 1 h, 30 µM AQ for 4 h, or 10 µM PYR for 1 h prior to VEGF (25 ng/ml) stimulation for 0, 2 or 5 min. Lysates were immunoblotted. Densitometry was performed, and the values below the rows of bands represent the ratio of phosphorylated protein to respective total protein. (B) Human VEGF-165 recombinant protein (VEGF; 25 ng/ml) stimulation of HUVECs promotes ZO-1 (green) disorganization at endothelial cell junctions (yellow arrows; left column; DMSO vehicle control pretreatment for 1 h prior to VEGF stimulation). ZO-1 organization is maintained upon pretreatment with 30 μM AQ for 4 h (magenta arrows; middle column) or 10 μM PYR for 1 h (magenta arrows; right column) prior to VEGF stimulation. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (C) Serum-starved human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAECs) were pretreated with 10 µM PYR for 1 h prior to VEGF (25 ng/ml) stimulation for 0, 5 or 30 min. VEGF stimulation promotes disorganization of ZO-1 (green) at endothelial cell junctions (yellow arrows). ZO-1 organization is maintained when HPAECs were pretreated with PYR (magenta arrows). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). (D) VEGF (25 ng/ml) stimulation of human lung microvascular endothelial cells (HMVEC-Ls) promotes ZO-1 (green) disorganization at endothelial cell junctions (yellow arrows). ZO-1 organization is maintained upon pretreatment with 20 μM PYR for 6 h prior to VEGF stimulation (magenta arrows). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). At least two biological replicates were performed for each experiment depicted in A-D. Scale bars: 20 µm.