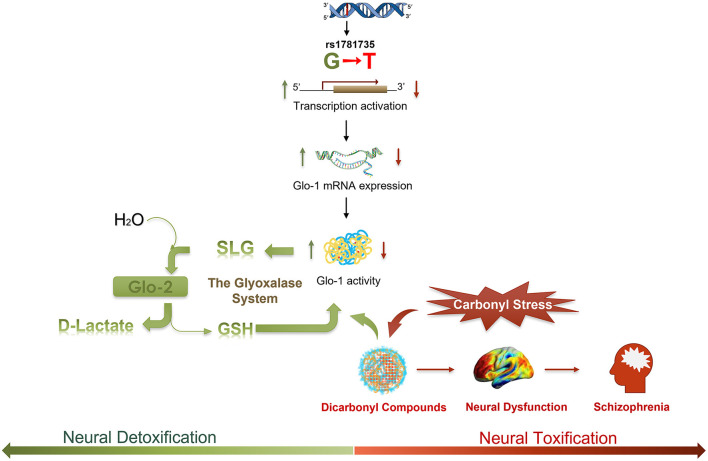
Figure 4.
A schematic illustrating the hypothesized regulatory process of the rs1781735 G-T mutation in the etiology of schizophrenia. Dicarbonyl compounds, such as methylglyoxal (MG), as a toxic species could lead to neural dysfunction and symptomatology in schizophrenia. Dicarbonyl compounds can be effectively detoxified via the metabolic pathway of the glyoxalase system. MG reacts with glutathione (GSH) and is converted to S-D-lactoylglutathione (SLG) by Glo-1. SLG is catalyzed into D-lactate by glyoxalase-2 (Glo-2), and GSH is recycled. As a rate-limiting enzyme in the glyoxalase system, Glo-1 plays a critical role in the detoxification of carbonyl stress in schizophrenia.