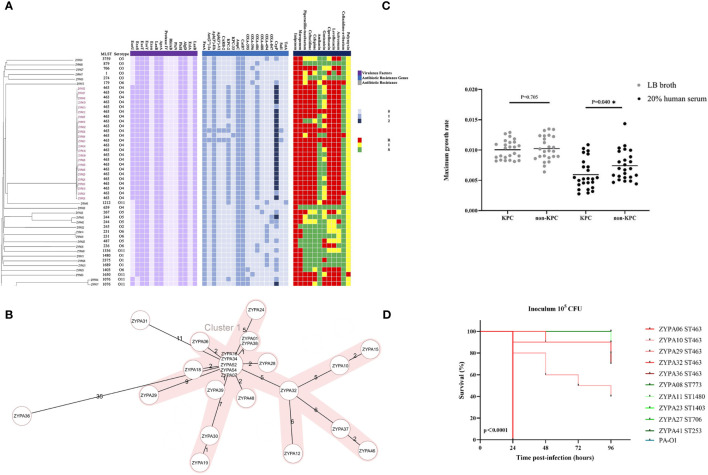
Figure 3.
(A) Genetic relatedness, antibiotic resistance genes, virulence factor determinants, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing results of 50 CRPA BSI strains. These features are shown separately on the four blocks of the picture. The gray value indicates the copy number of the antibiotic resistance gene and virulence factors bla KPC-2 and ST463 are highly associated (22 out of 24; 91.7%). R, resistant; I, Intermediate; S, Sensitive; (B) Minimum spanning trees of 24 ST463 CRPA BSI strains from cgMLST analysis. Distance based on 4823 targets genes with pairwise ignore missing values. CgMLST profiles are represented by circles. The shaded parts represent the same cluster with a distance threshold of 10. The size of the circle is proportional to the number of isolates sharing the same cgMLST profile, with the biggest one including five isolates; (C) Neutrophil-killing resistance; at the maximum growth rate of KPC and non-KPC group; (D) Virulence potential in a G mellonella infection model. Five isolates of ST463 and five isolates of other STs representing various genetic background were randomly selected for the infection assay at 105 CFU. P values were calculated by log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Each line represents a single isolate. Isolate PA-O1 was used as the control. Abbreviation: CFU, colony-forming units.