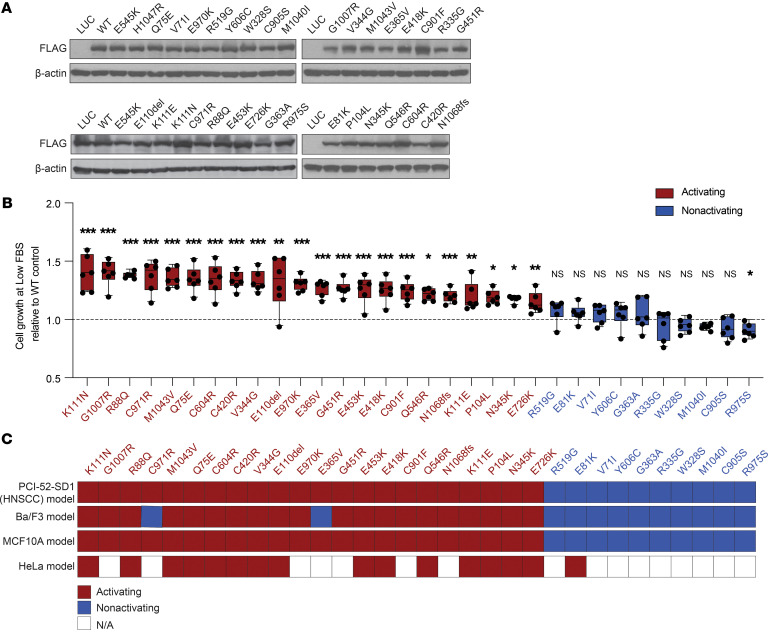
Figure 3. Functional characterization of all 32 noncanonical PIK3CA mutations in the HNSCC serum-dependent model.
(A) Generation of isogenic PCI-52-SD1 cells expressing the 32 noncanonical PIK3CA mutations. Immunoblotting with anti-FLAG was used to confirm expression of LUC, WT p110α, or the indicated p110α mutants following growth in the presence of Dox (1 ug/mL) for 24 hours; β-actin, loading control. (B) Serum-dependency assays. Cells were cultured for 72 hours in medium containing Dox (1 μg/mL) with either normal FBS (10%) or low FBS (1%–2%) followed by crystal violet assays. Shown is the growth of cells cultured in the medium containing low FBS relative to the individual control of normal FBS (n = 6) followed by normalization to WT PIK3CA control. The dashed line represents the significance limit set as the value equal to WT PIK3CA. Mutants were classified as activating if they exhibited statistically enhanced cell growth in low serum compared with WT PIK3CA. Data are represented as box and whiskers. The whiskers go down to the minimum and up to the maximum value and plot each individual value as a point superimposed on the graph. The box extends from the 25th to 75th percentiles. The lines within the boxes represent the median value. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, NS ≥ 0.05 for 1-tailed Student’s pairwise t test. The experiment was repeated 3 times with similar results. (C) Heatmap indicating the concordance of functionality conferred by HNSCC-associated noncanonical mutations tested in different cell line models. The mutations were assigned as “activating” if they exhibited an activity significantly higher than WT; otherwise, the mutations were annotated as “nonactivating.”