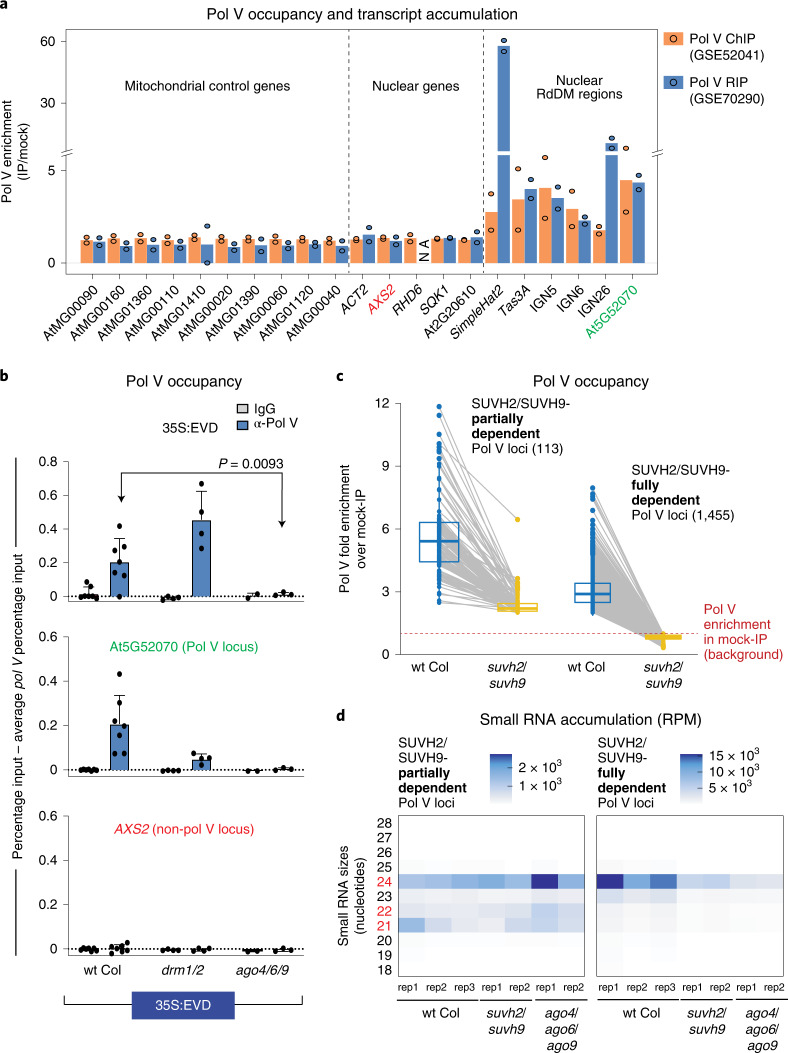
Fig. 3. The first round of Pol V recruitment requires an AGO4-clade protein.
a, Reanalysis of ChIP and RIP data of Pol V occupancy and transcription. Mitochondrial negative control genes, nuclear genes and nuclear positive control RdDM regions are shown. Two replicates are shown as dots, and their average is the height of the bar. NA, not applicable due to absence of any mapping reads in the IP or the mock samples. Genes with coloured labels are used as controls in ChIP experiments. b, Pol V ChIP of 35S:EVD T1 plants as percentage input minus the background of percentage input in T1 pol V mutants. At least three biological replicates were used for each genotype: seven for wt Col, four for drm1/2 and three for ago4/6/9. At5G52070 is a locus that undergoes RdDM and serves as a positive control for Pol V occupancy32, while AXS2 is a gene that does not undergo RdDM and serves as a negative control. Error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed unpaired t-test with Welch’s correction. c, Box plot with connected data points of Pol V occupancy comparing wt Col (blue) and suvh2/suvh9 double mutants (yellow). Pol V occupied regions are categorized into SUVH2/SUVH9-partially and -fully dependent loci (Methods). Pol V occupancy is displayed as fold enrichment over mock-IP. Grey lines represent the change in Pol V enrichment between wt Col and suvh2/suvh9 for each locus. Box plots represent 25th and 75th percentile with whiskers at 10th and 90th percentile values, and the median is represented by a line. d, Heatmap of small RNA sequencing for Pol V occupied loci that are categorized as either SUVH2/SUVH9-partially or -fully dependent from c.