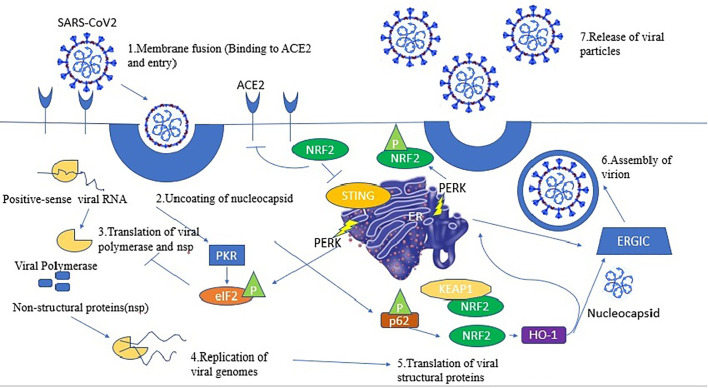
Fig. 1.
This reflects the various steps of viral cycle (1) The viral spike (S) protein binds to to ACE2 causing virion entry (2) Uncoating of the viral nucleocapsid in the cytoplasm of the host cell. (3) Specific viral proteins are formed as a result of translation of the viral positive-sense single-stranded RNA (+ssRNA) and final cleavage of the translation product. The DNA/RNA sensor cGAS is activated by the viral RNA inside the host cell, which signals through the adaptor STING, and leads to induction of type I and type III interferons (IFNs). In turn IFN production is repressed by NRF2 by downregulation of STING expression [56]. (4) NRF2 brings about induction of HO-1 expression, producing Fe2+ that could bind to the divalent metal-binding pocket of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) of SARS-CoV2 and inhibit its catalytic activity bringing about replication of viral genome (5) Double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase R (PKR) conducts the host defense, which also phosphorylates eIF2 and inhibits protein translation. p62 is phosphorylated by PKR, thus bringing about NRF2 activation upon removal of its repressor KEAP1 by autophagy. Inhibition of protein translation in turn activates the unfolded protein response (UPR). PERK, a crucial Ser/Thr protein kinase in UPR signaling, brings about NRF2 phosphorylation leading to its stabilization and increased transcriptional activity (6) Virion assembly (7) Release of viral particles. Abbreviations: ACE2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; eIF2, eukaryotic initiation factor 2; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; ERGIC, ER–Golgi intermediate compartment; HO-1, heme oxygenase 1; IFN, interferon; KEAP1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2 p45-related factor 2; PERK, PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; P, phosphorylation; PKR, protein kinase R; STING, stimulator of interferon genes[141]