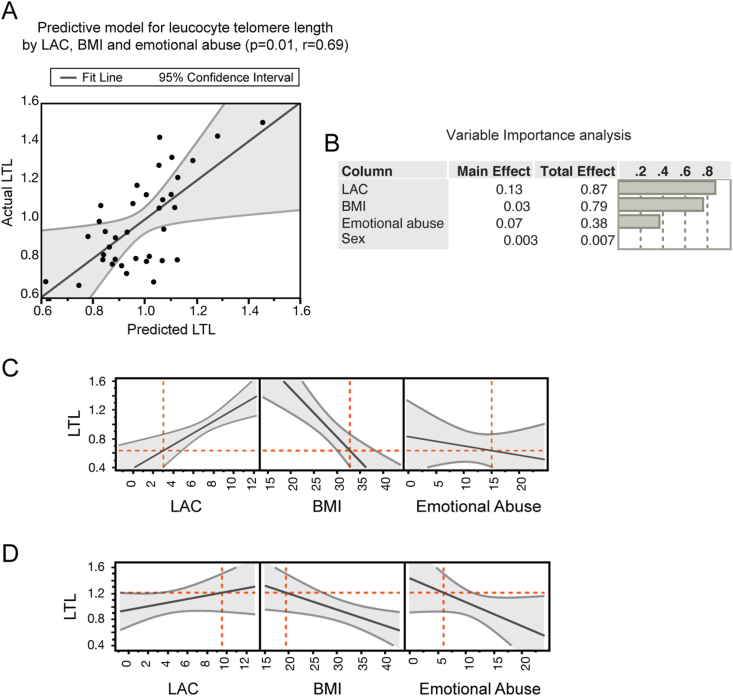
Fig. 2.
Multidimensional biological pathways in potential mitochondrial endophenotypes of depression. A, Multifactorial regression analysis showed that multidimensional factors, including LAC levels, BMI and reported rates of childhood emotional abuse predict leucocytes telomere length (LTL) in subjects with MDD. The model in A depicts LTL predicted values in X and LTL actual values in Y. B Variable importance analysis indicated that the integration of the individual measures results in a superior predictive potential in relation to telomere length as showed by the higher total effects of each variable than the corresponding main effects. C and D, Prediction profilers showed the directionality of the association between the multidimensional measures of mitochondrial metabolism (i.e., LAC levels), metabolic function (i.e., BMI), cellular aging (i.e., LTL), and environmental stress (i.e., childhood trauma). Specifically, we found the lowest LAC levels in those subjects with elevated BMI, high reported rates of childhood emotional abuse and decreased LTL; vice versa subjects with the highest LAC levels are characterized by decreased BMI, low rates of emotional abuse and increased LTL as shown in panel D.