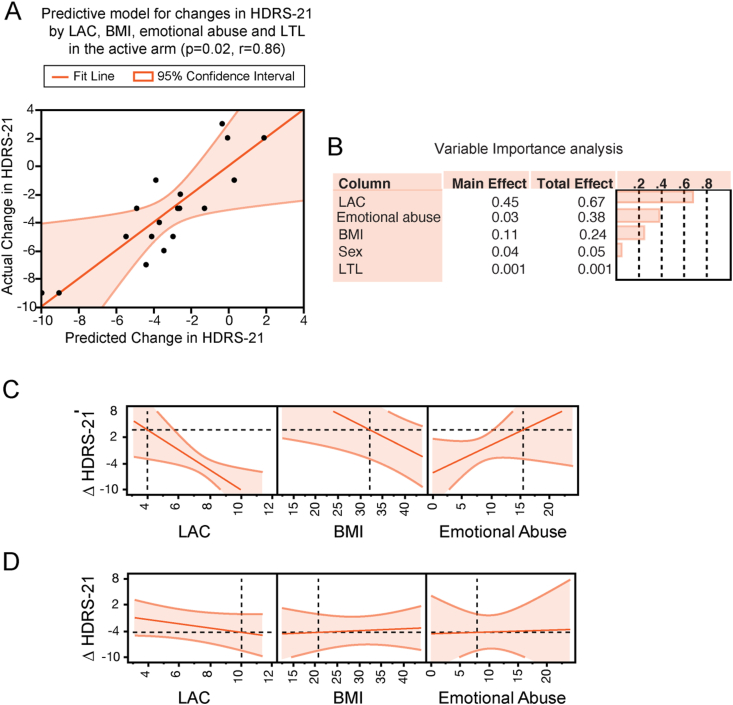
Fig. 3.
Multidimensional predictors of antidepressant responses to pioglitazone in patients with MDD. A, multifactorial regression analysis showed that baseline LAC levels, BMI, LTL and reported rates of childhood emotional abuse predict changes in depression severity in the responses to pioglitazone as assessed using the HDRS-21. A negative change in HDRS-21 indicates improvement in depression severity. The predictive model depicts actual changes in HDRS-21 in Y and predicted changes in HDRS-21 in X as predicted by the interactions between LAC, BMI, emotional abuse, and LTL. B, Variable importance analysis indicated that, of all parameters, LAC levels had the highest variable importance (0.447) in the model predicting changes in depression severity in response to treatment with pioglitazone. Of note, the total effects of each variable were higher than the corresponding main effects. C and D, Prediction profilers show the directionality of changes in depression severity after treatment with pioglitazone as predicted by the interaction of baseline measures of LAC levels, BMI and emotional abuse in a model controlled for LTL. Specifically, decreased baseline LAC levels, elevated BMI and high reported rates of emotional abuse predict lack of changes in depression severity (panel C), vice versa increased baseline LAC levels, decreased BMI and low reported rates of emotional abuse predict decreased depression severity at the HDRS-21 in the responses to pioglitazone (panel D). Both the prediction profilers in B and C are controlled for LTL.