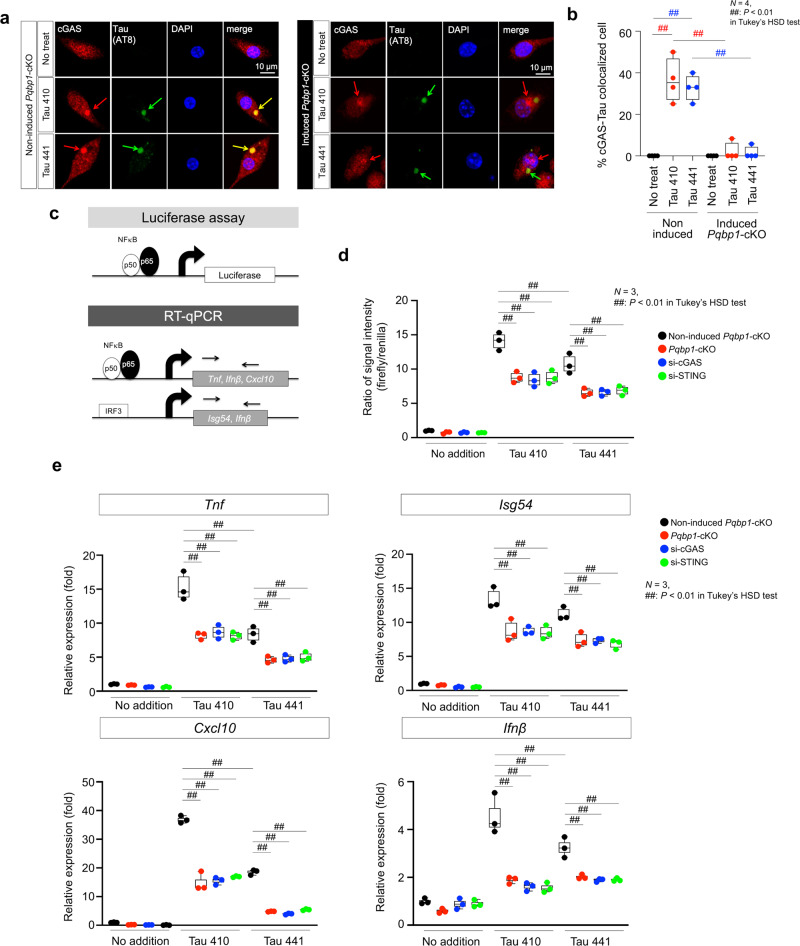
Fig. 5. PQBP1 is essential for recruiting cGAS to Tau.
Confocal microscopy images of primary Pqbp1-cKO microglia stained with anti-cGAS and -tau antibodies. a Cytoplasmic tau foci after incorporation recruit cGAS in the presence of PQBP1 (left panels), while in the absence of PQBP1, cGAS is mislocalized and not merged with cytoplasmic foci of tau, which is phosphorylated after endocytosis. b Quantification of cGAS-tau colocalized cells in four wells of non-induced and tamoxifen-induced Pqbp1-cKO microglia after tau addition to primary culture medium. N = 4. ##P < 0.01 in Tukey’s HSD test. c Schemes showing the concepts of the luciferase assay used to monitor NFκB activity under tau stimulation and PQBP1–cGAS–STING pathway perturbation (d) and of RT-qPCR used to monitor expression levels of NFκB-target genes (e). d Luciferase assay to monitor NFκB activity under Tau 410/441 stimulation together with PQBP1–cGAS–STING pathway perturbation by tamoxifen-induced Pqbp1-cKO, siRNA against cGAS and siRNA against STING. N = 3. ##P < 0.01 in Tukey’s HSD test. e RT-qPCR to monitor expression levels of NFκB- or IRF3-target genes (Tnf, Isg54, Cxcl10, and Ifnβ) under Tau 410/441 stimulation together with PQBP1–cGAS–STING pathway perturbation by tamoxifen-induced Pqbp1-cKO, siRNA against cGAS, and siRNA against STING. N = 3. ##P < 0.01 in Tukey’s HSD test. Box plots show the median, quartiles, and whiskers that represent data outside the 25th to 75th percentile range.