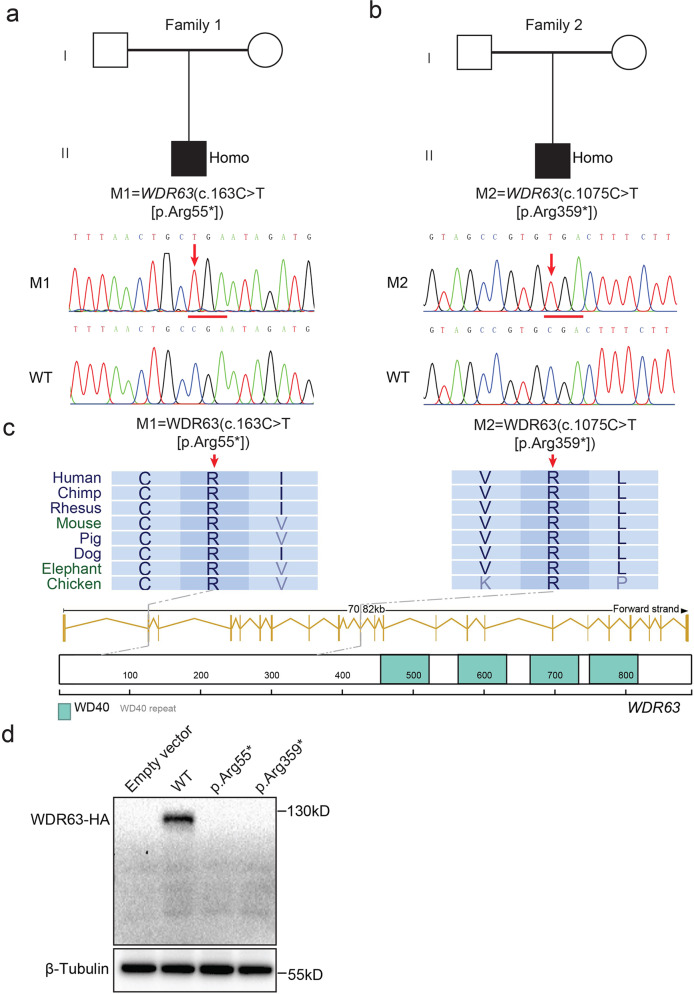
Fig. 1. Identification of bi-allelic variants of WDR63 in patients with MMAF.
a, b Pedigree of family 1 affected by bi-allelic WDR63 variant that was identified by WES from MMAF-affected men (a). Pedigree of family 2 affected by bi-allelic WDR63 variant that were identified by Sanger sequencing from NOA-affected men (b). Filled black filled squares indicate infertile men in this family. Sanger sequencing results are shown under the pedigrees. The mutated positions are indicated by red arrows. c Schematic representation of the domains of WDR63 and locations of WDR63 variants identified in this study. Sequence alignment shows conservation of the mutated residues across different species according to UCSC genome browser. The green boxes indicate Trp-Asp (WD40) repeat domains as described by the UniProt server. d WDR63 variants cause the degradation of WDR63 protein. Full-length wild-type and mutant WDR63 cDNA constructs were overexpressed in HEK293T cells followed by immunoblotting analysis. Abbreviations: M1, mutation 1; M2, mutation 2; Homo, homozygous; WD40, Trp-Asp repeat.