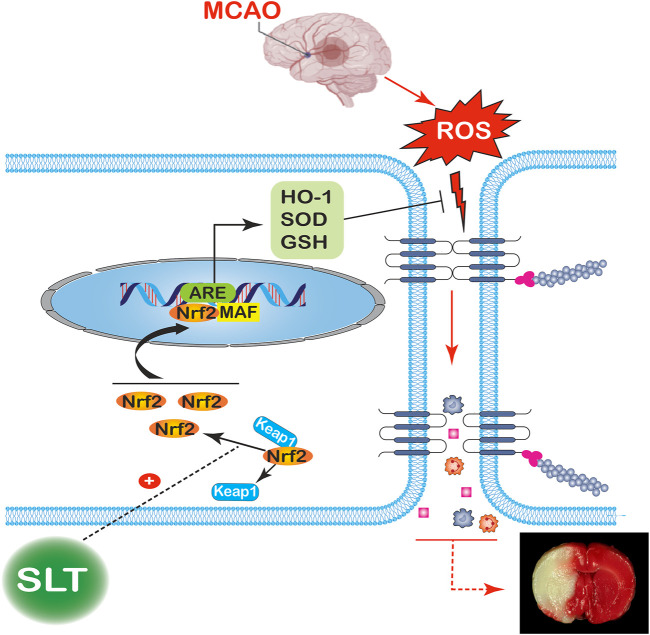
FIGURE 9.
Putative mechanism for the therapeutic effect of SLT on brain ischemia. Occlusions in the cerebral arteries induce a drastic elevation in ROS contents; the excess ROS severely disrupts the brain blood barriers, leading to serious leakages from the blood vessels and brain edema, finally resulting in an infarction of large volume. SLT dramatically releases Nrf2 detained in the cytoplasm and promotes its nucleus translocation, thus priming the downstream transcriptions and increasing the contents of HO-1, SOD, and GSH, which then lead to massive elimination of ROS, cutting off the injury cascade and finally rescuing the brain from ischemia.