Figure 1.
Megakaryocyte-specific Rbm8a knockout impairs platelet production
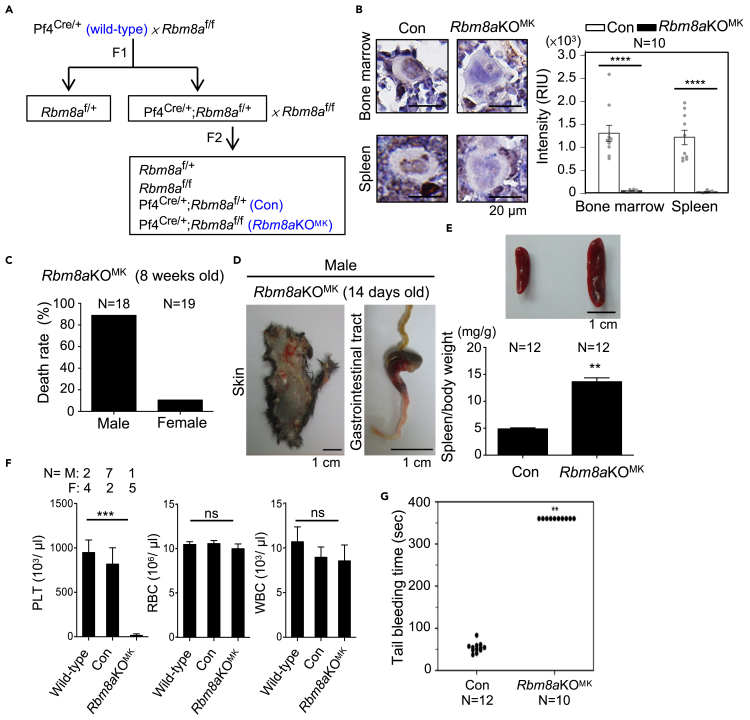
(A) Schematic diagram illustrating the generation of megakaryocyte-specific Rbm8a knockout mice.
(B) Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining for Y14 in the sections of bone marrow and spleen from 9-week-old Con and Rbm8aKOMK mice, magnified images (from Figure S1C) of representative cells are shown. Bar graph with overlapping dots shows the relative intensity unit (RIU; mean ± SEM) of Y14 in megakaryocytes from Con and Rbm8aKOMK bone marrow and spleen measured by using ImageJ. N, sample number; ∗∗∗∗p<0.0001.
(C) Death rate of 8-week-old male and female Rbm8aKOMK mice.
(D) Subcutaneous tissue (skin) and gastrointestinal tract of 14-day-old male Rbm8aKOMK mice.
(E) The spleen/body weight ratio (mg/g; mean ± SEM, N = 12 in each group, ∗∗p < 0.01) of 10- to 12-week-old mice.
(F) Hematological analysis of blood from 6- to 8-week-old mice of the indicated genotypes (mean ± SEM). N, sample number; M, male mice; F, female mice; ns, not statistically significant; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.
(G) Tail bleeding time of 8- to 10-week-old Con and Rbm8aKOMK mice was recorded up to 6 min. N, sample number; ∗∗p < 0.01.