Figure 2.
Rbm8a knockout impairs megakaryopoiesis
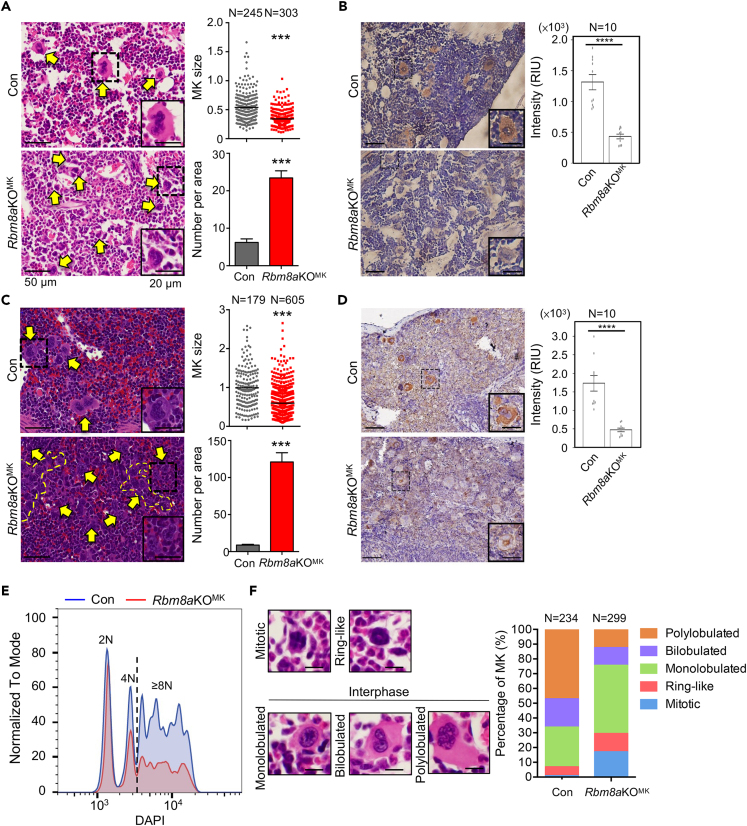
(A and B) Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining was performed using bone marrow sections from 9-week-old Con and Rbm8aKOMK mice. Yellow arrows indicate megakaryocytes. A selected megakaryocyte in the dashed-line square is magnified in the inset. The dot plots shows the size of megakaryocytes measured from H&E staining (1.0 = 500 μm2); for each, N indicates the number of cells from five mice of each genotype (mean ± SEM) that were measured. The bar graph shows the number of megakaryocytes in a 0.15 mm2 area; mean ± SEM was calculated from five areas each. ∗∗∗p < 0.001. MK, megakaryocyte. Scale bars in panels B, C, and D are the same with panel (A).
(B) IHC staining was performed using anti-vWF in the bone marrow as in panel (A). Bar graph with overlapping dots shows the level of vWF as measured in Figure 1B.
(C) H&E and IHC of the spleen sections from 9-week-old Con and Rbm8aKOMK mice were respectively performed as in panels A and (B). In panel C, yellow dashed lines indicate a cluster of megakaryocytes. The dot plots and bar graph were as in panel (A).
(D) IHC staining was performed using anti-vWF in the spleen as in panel (C). The level of vWF was measured as in Figure 2B.
(E) A representative DNA content histogram of bone marrow cells (megakaryocytes) from Con and Rbm8aKOMK mice. Quantitative analysis is shown in Figure S1E.
(F) Stacked-column bar shows the proportion (%) of each nuclear shape of Con and Rbm8aKOMK megakaryocytes. Representative images of the different nuclear shapes were obtained from Con mice. All images were collected from five mice for each genotype.