Figure 5.
p53 inhibition reverses the differentiation defects of Rbm8aKOMK megakaryocytes
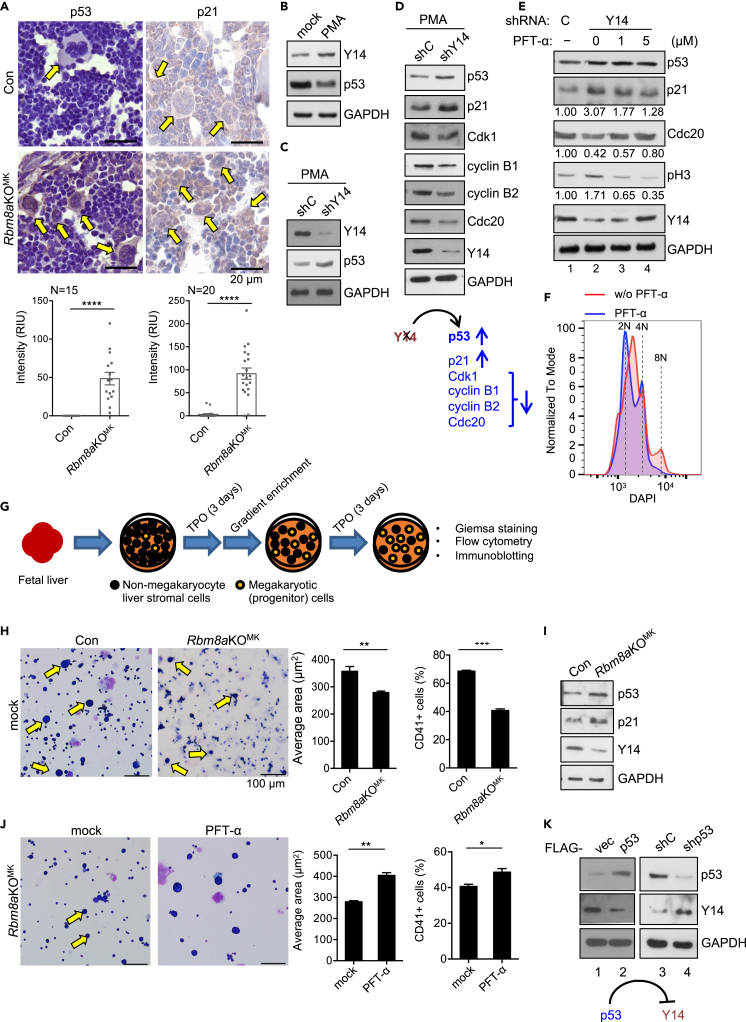
(A) IHC staining of Con and Rbm8aKOMK bone-marrow sections using antibodies against p53 and p21; their relative level was measured as in Figure 1B.
(B) HEL cells were mock- or PMA-treated for 3 days. Immunoblotting was performed to examine Y14 and p53 proteins.
(C) HEL cells were transduced with control or shY14-lentivirus, followed by PMA induction. Immunoblotting was performed as in panel (B).
(D) HEL cells were treated as in panel C; immunoblotting was performed using antibodies against indicated proteins. A diagram shows that Y14 depletion increases the expression of p53 and 21 and decreases the expression of four cell-cycle regulators examined.
(E) HEL cells were transduced as in panel C followed by mock (−) or PFT-α (1 or 5 μM) treatment. The relative levels of p21, Cdc20, and phospho-H3 (pH3) are indicated below the respective blots.
(F) HEL cells were transduced with shY14-lentivirus and treated with PMA followed by mock or PFT-α treatment. DNA histogram analysis was performed as in Figure 2E.
(G) The diagram depicts isolation and culture of megakaryocytes from E14.5 fetal liver. Isolated fetal liver stromal cells were cultured for 3 days in the presence of thrombopoietin (TPO). Megakaryocytes were enriched and cultured for another 3 days in the presence of TPO and then subjected to different analyses (panels H and I).
(H) Giemsa staining of an enriched fraction containing megakaryocytes (yellow arrows). Bar graphs show the average size (μm2) of >350 cells (middle panel) and the percentage of CD41+ (right panel); experiments were performed in triplicate (mean ± SEM; ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
(I) Immunoblotting of the megakaryocyte-containing fraction was performed using antibodies against indicated proteins; residual Y14 signal was from nonmegakaryocytes in the coculture.
(J) As in panel H, the megakaryocyte-containing fraction was mock- or PFT-α treated, followed by Giemsa staining or flow cytometry using anti-CD41. Bar graphs are shown as in panel F (mean ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01). Scale bars in panel G are the same as that in panel (F).
(K) Immunoblotting was performed in HEL cells that were transfected with the empty (vec) or p53-expressing vector (lanes 1–2) or transduced with control (shC) or p53-targeting shRNA (shp53) lentivirus (lanes 3–4). A diagram shows that p53 suppresses Y14 expression.