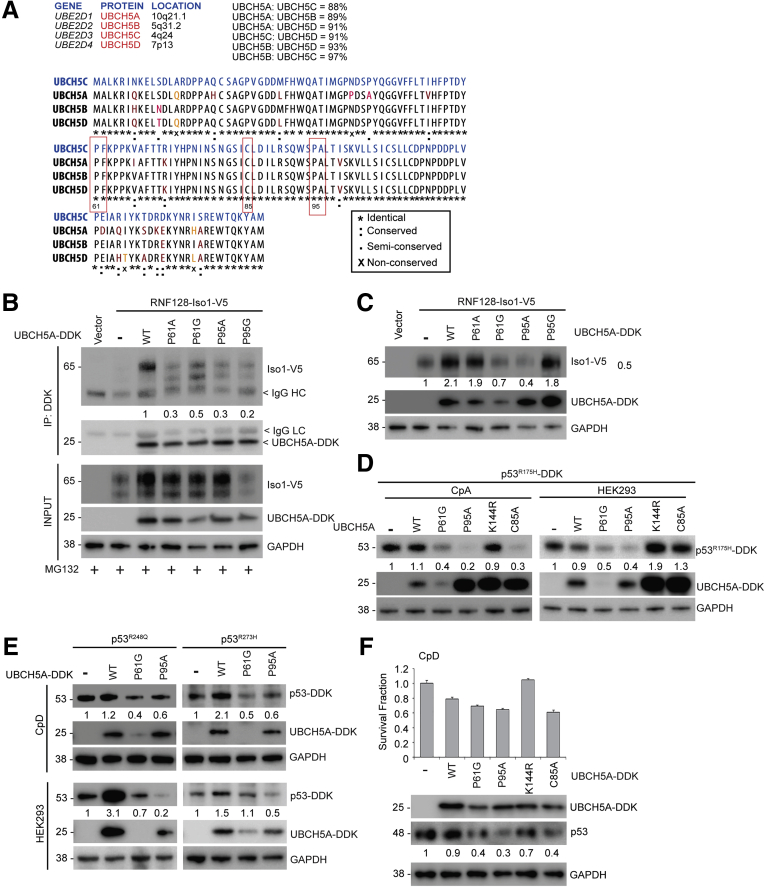
Figure 8.
Targeting of RNF128 Iso1 via alteration of UBCH5A catalytic activity to destabilize mutant p53. (A) Upper left panel: Table showing UBE2D family member genes (UBE2D1–4), protein (UBCH5A–D) and their respective chromosomal locations. Upper right panel: Percentage sequence homology between UBCH5 family members. Lower panel: Pairwise amino acid sequence alignments between UBCH5A–D isoforms performed using the CLASTALW multiple sequence alignment tool. Redboxes identify 61PF62, C85. and 95PA96 residues as discussed in the article. (B) The RNF128 Iso1-V5 constructs were co-expressed with the indicated UBCH5A mutants (WT, P61A/G, and P95A/G). Twenty hours after transfection, cells were treated with MG132 as described earlier, followed by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting as indicated. (C) Similar co-transfection was conducted in CpA cells as described earlier and cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. (D) CpA (left panel) and HEK293 (right panel) cells overexpressing P53R175H-DDK mutant were co-transfected with different UBCH5A mutants as indicated and 48 hours after transfection mutant p53 levels were determined using immunoblotting as indicated. (E) As described earlier, p53R248Q and p53R273H mutants showed down-regulation upon overexpression of P61G and P95A mutant UBCH5A in CpD (upper panel) and HEK293 cells (lower panel). (F) UBCH5A (WT, P61G, P95A, K144R, and C85A mutants) were overexpressed in CpD, and 48 hours after transfection cells were plated at clonal density to perform a clonogenic assay. Survival fractions upon UBCH5A overexpression are shown in the top panel and the corresponding cell lysates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using the indicated antibodies. DDK, DYKDDDDK tag; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; IP, Immunoprecipitation.