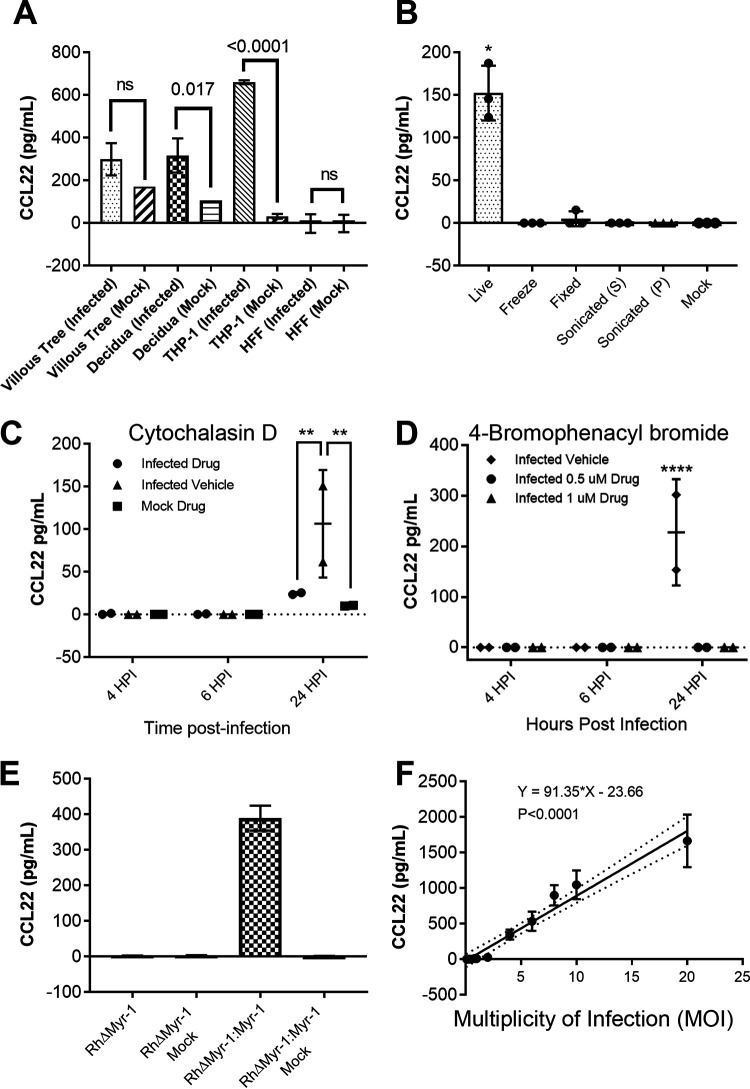
FIG 1.
(A) THP-1 cells, human foreskin fibroblasts (HFFs), and second trimester placental samples of villous trees and decidual tissue were infected with a type 1 strain of Toxoplasma gondii (RH:YFP). Statistics on the THP-1 cell and HFF cell samples were performed by ordinary two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. Statistics on the placental samples were performed by two-tailed Welch-corrected t tests. (B) Type 1 strain (RH) T. gondii parasites were subjected to multiple treatments as described in Materials and Methods. The soluble fraction of the sonicated treatment is denoted by S; the insoluble fraction is denoted by P. THP-1 cells were then exposed to either live parasites or treated parasites. Statistics were performed by multiple two-tailed Welch-corrected t test comparisons with the live parasite treatment at a P of ≤0.0145. (C and D) Type 1 strain (RH) T. gondii parasites were treated with either cytochalasin D (C) or 4-bromophenacyl bromide (D) as described in Materials and Methods. THP-1 cells were then infected with the respective parasite treatment. Statistics were performed by two-way ANOVA and multiple-comparison post hoc tests, where the Cyt-D P value is 0.009, and the 4-BPB P value is <0.0001. (E) Type 1 strain (RH) T. gondii parasites deficient in Myr-1 (TgRHΔMyr-1) and their complement (TgRHΔMyr-1:Myr-1c) were used to infect THP-1 cells. (F) Type 1 strain (RH) T. gondii parasites were used to infect THP-1 cells at MOIs of 20, 10, 8, 6, 4, 3, 1, 0.8, 0.4, 0.2, and 0.1. (A to D) The respective cells/tissues were infected at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 3. Supernatants were collected at 24 h postinfection unless indicated otherwise and assayed by CCL22 ELISA.